What is PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL - relational database system founded on SQL-queries language. Common standards following and possibility to make high performance systems is reason why PostgreSQL is popular today.
Before installation
To install PostgreSQL you should have:
- Server with at least 1 CPU cores, 1Gb of RAM and 10Gb drive space. Real requirements may be some differ and depends of your application needs and optimization;
- Actual operation system (Centos 7 in this article);
- Administrative account access.
Setup process
To install PostgreSQL on your server please do all steps below:
- Update current system software:
yum -y update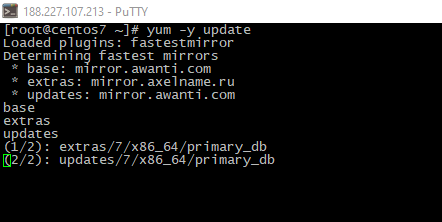
- Reboot the server to use the newest packages;
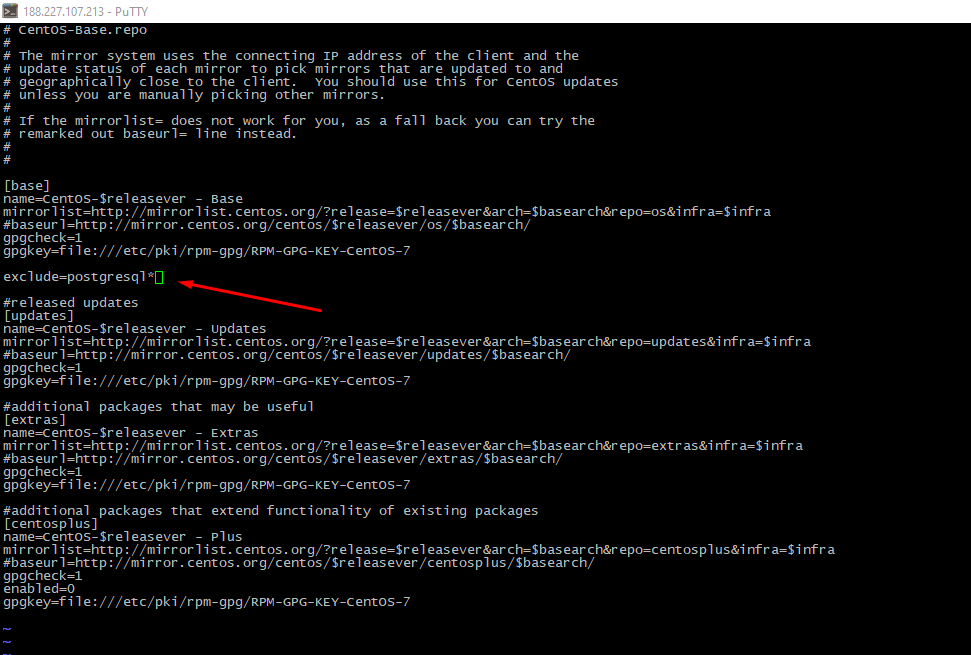
- Add exception to the "base" section of /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo repository file otherwice old version PostgreSQL will be installed:
- Add PostgreSQL repo and find the latest version:
yum -y install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm; yum list -y postgre*-server*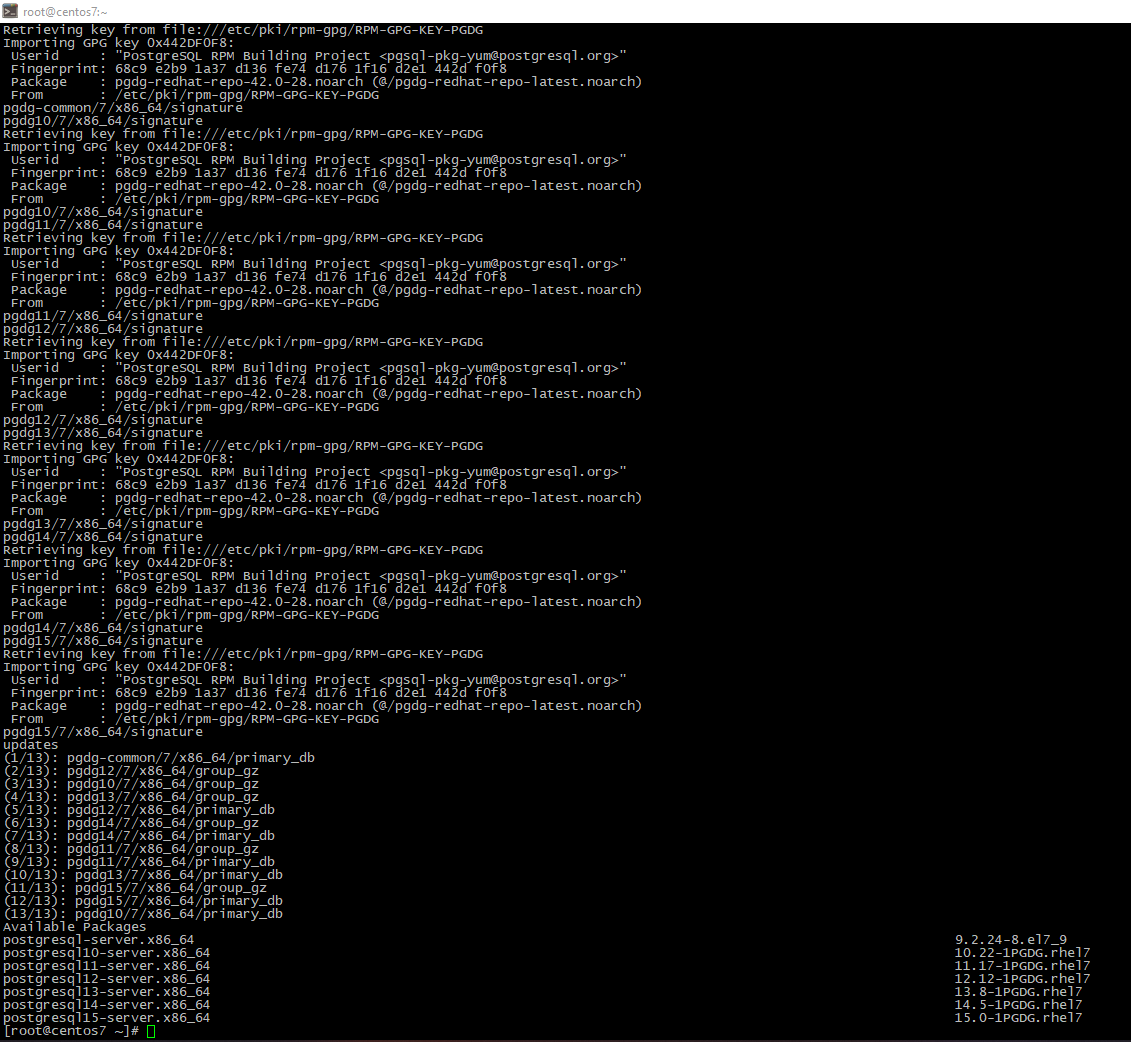
- As shown at the previous screenshot, last PostgreSQL version is 15. Let's install it:
yum -y install postgresql15-server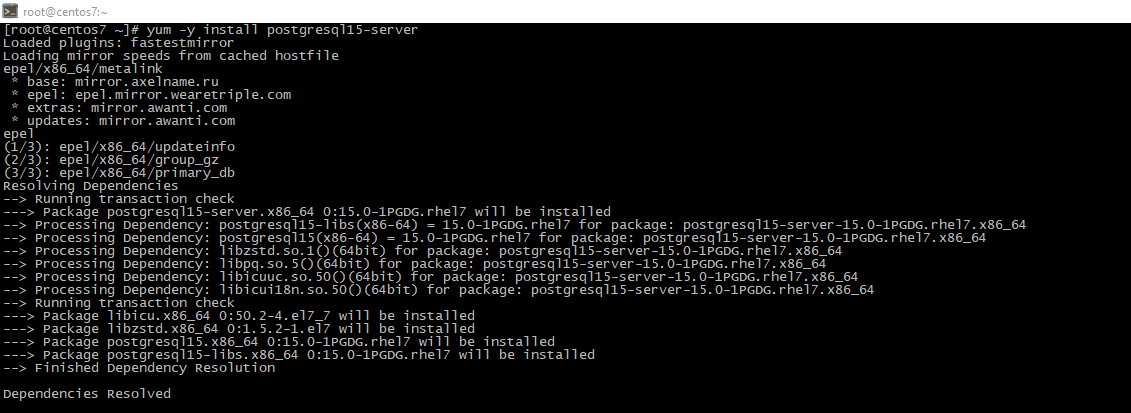
NOTE: in case dependancy resolution failed, you should install epel repository then try to install PostgreSQL again:
yum -y install epel-release- Initialize new DB-cluster:
/usr/pgsql-15/bin/postgresql-15-setup initdb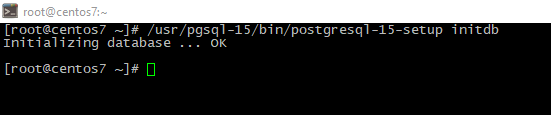
- Enable launch at system boot and run the service:
systemctl enable postgresql-15; service postgresql-15 start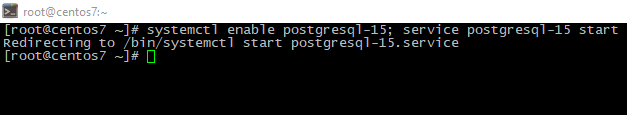
- Check the status:
service postgresql status 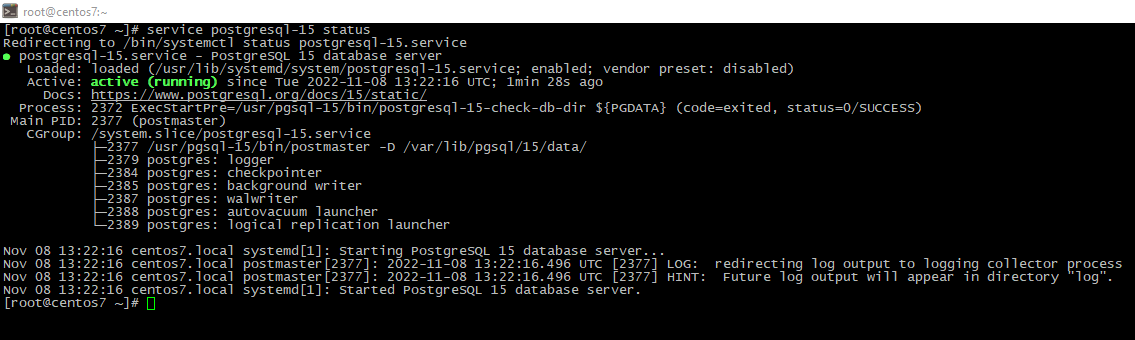
Data operations
- To create database you should use built-in administrative account:
su postgres
psql postgres
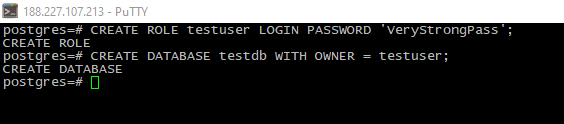
- Create the user role and test database:
CREATE ROLE <username> LOGIN PASSWORD '<password>';
CREATE DATABASE <dbname> WITH OWNER = <username>;
- Login as created user:
psql -h <host> -d <dbname> -U <username> -p <PostgreSQL_port> 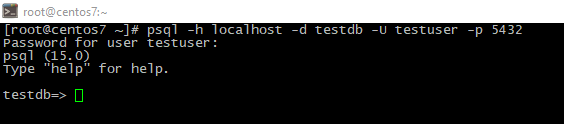
- Let's try to create table into our new database:
CREATE TABLE testtable (
item_num integer NOT NULL,
item_name character varying(50) NOT NULL,
item_detail character varying(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (item_num)
);
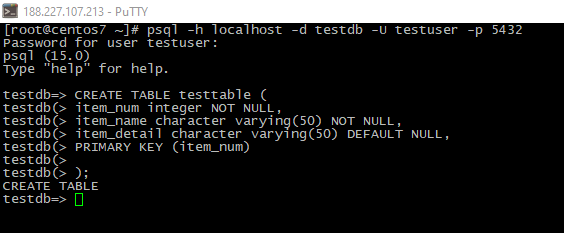
I created a table with three columns, item_num (digit), item_name (text) and item_detail (text, may be empty).
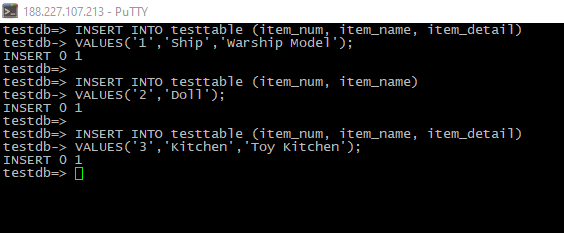
- Data insert:
INSERT INTO testtable (item_num, item_name, item_detail)
VALUES('1','Ship','Warship Model');
INSERT INTO testtable (item_num, item_name)
VALUES('2','Doll');
INSERT INTO testtable (item_num, item_name, item_detail)
VALUES('3','Kitchen','Toy Kitchen');
- Check our job:
SELECT <content> from <table_name>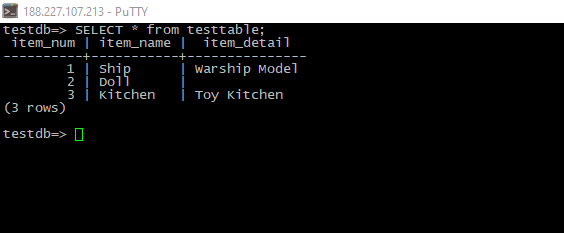
Instead of final
In this tutorial I showed how to install PostgreSQL on Centos 7 and operate with data "inside" the database.




