Introduction
Linux systems are commonly managed through the command-line interface (CLI), which provides speed, flexibility, and precise control over system operations. Because Linux uses a modular filesystem structure with thousands of files and directories, locating a specific file can be challenging.
The find command is a built-in Linux utility designed to search for files and directories using flexible and powerful criteria.
Requirements
- Linux system (Debian 12 or newer);
- Root or sudo privileges (optional, depending on search scope);
- Basic knowledge of Linux command-line us
Basic Usage of the find Command
Let's imagine we have backup in our system which name is BACKUP.txt in one of the tonne of data, then we need to check installation of command:
find --help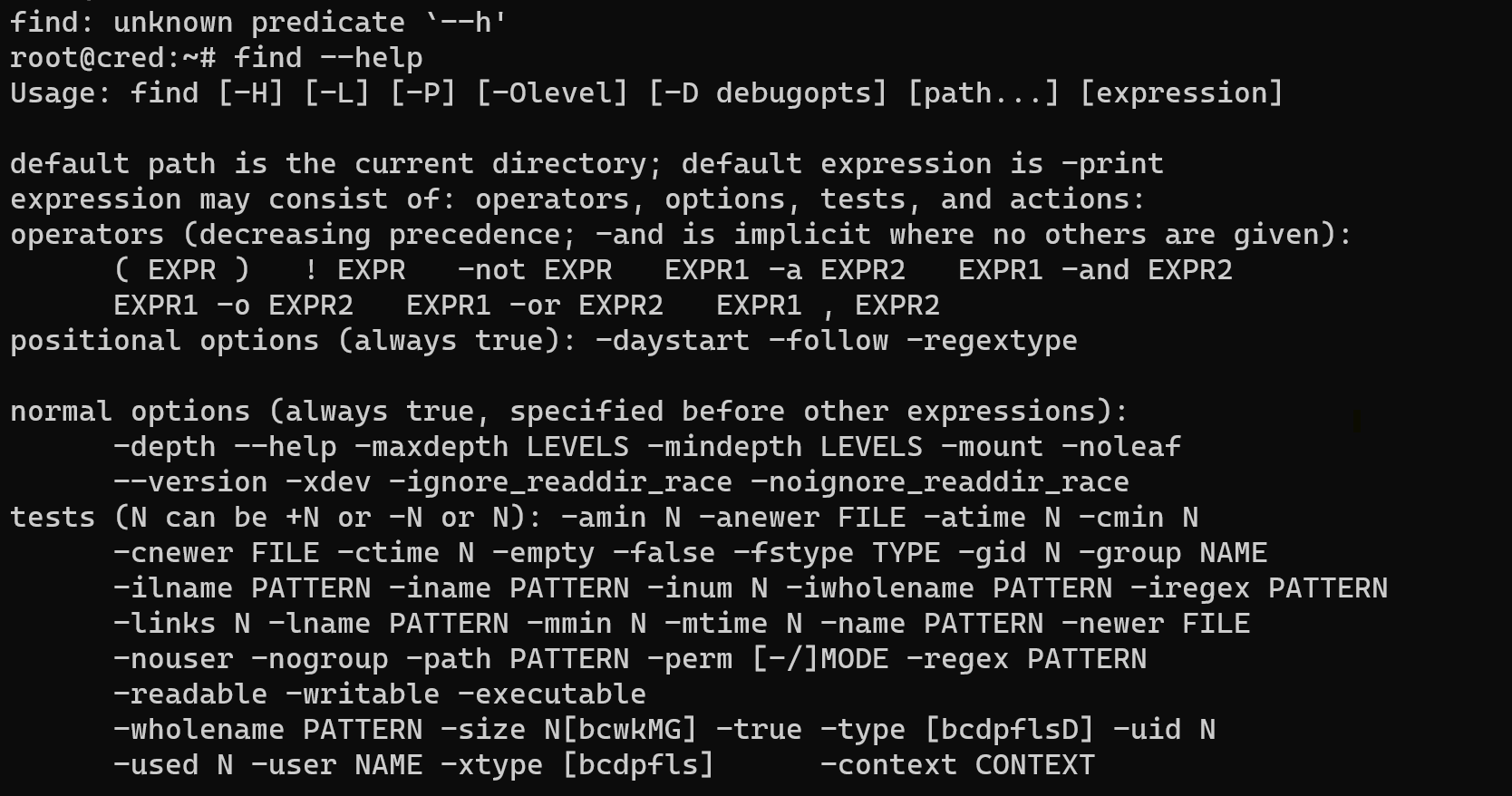
Alright, utility was in the system before, now we can use command below for search needed object:
find / -name "BACKUP.txt" This command searches for an exact filename starting from the root directory.
But if you don't remember format of your backup file, then you can mask for searching:
find / -name "BACKUP.*" Note: The -name option is case-sensitive. Use -iname for case-insensitive searches:
find / -iname "backup.*"Alternatively, if you search by only format, then you can use command below:
find / -name "*.txt" 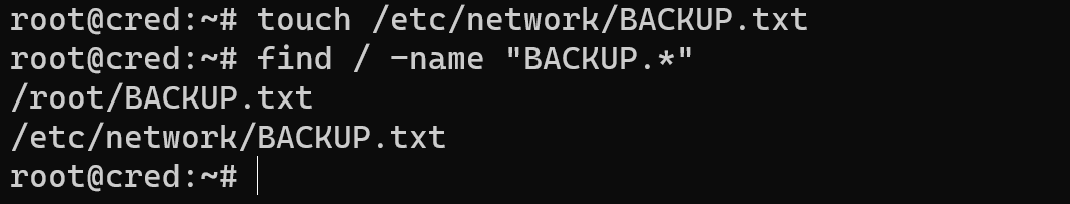
We can see two path in the whole file system and in the command we indicate / like as root of all machine. But what if you don't remember name and type of file, but you highlight, that creating was day ago, type command:
find /data -mtime -1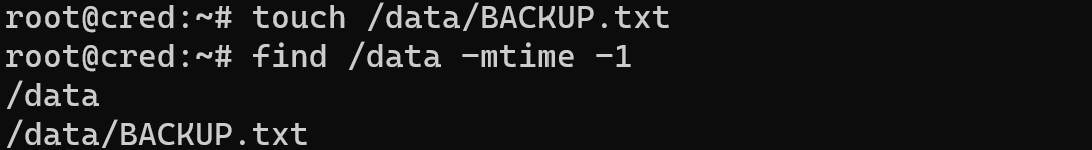
If we want search only file then use accordance option and we also can combine this:
find /data -type f -mtime -1 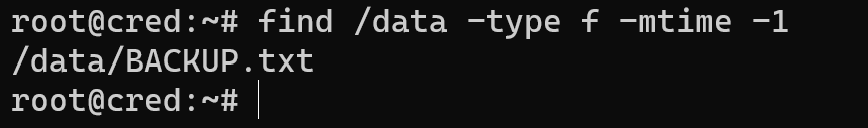
The Mtime that decoding as modification time and we can see that text file, if we remember only a size of saved file we can use:
find /data -size -1M 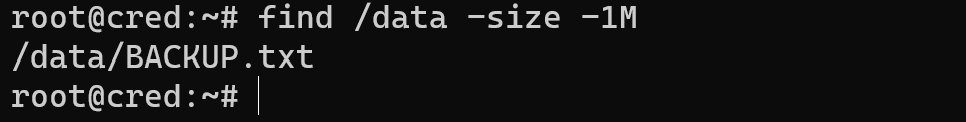
But if you remember only specific data, for example, you denied access for all group and users with exception owner to the file. Then use command below:
find /data -type f -perm 700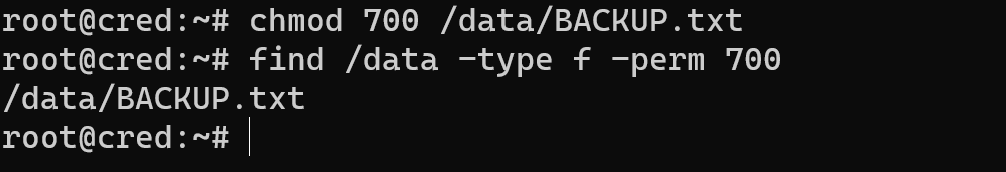
Conclusion
The Linux find command is a powerful and flexible tool for locating files and directories based on various criteria such as name, type, size, permissions, and modification time. Mastering find allows administrators and users to efficiently navigate large and complex filesystems and automate file management tasks.



