Python is a widely used high-level programming language known for its performance, flexibility, and extensive ecosystem. It is commonly used for web development, automation, data processing, and running large-scale applications in production environments.
Installing the latest stable version of Python on a CentOS server is straightforward when done correctly. In this guide, we will install Python 3.11.x (the latest stable release at the time of writing) by compiling it from source, ensuring compatibility, stability, and safe coexistence with the system’s default Python version.
Updating Operating System Packages
Before updating Python directly, we update the operating system. Navigate terminal then execute:
sudo dnf updatesudo dnf upgrade
Installing Python on CentOS
To work with Python you need to install it on your computer, which can be a non-trivial task for Linux newbies. At this point, we'll walk via the installation step by step and provide detailed tutorial with commands and descriptions of each step.
Installing additional packages
If your system does not have the "wget" module, execute the commands one after the other:
sudo yum search wgetsudo yum install wget
For further work, you need to get packages:
yum install gcc yum-utils zlib-devel python-tools cmake git pkgconfig -y --skip-brokenAfter successfully completing the installation, let's install the "Development Tools"
yum groupinstall -y "Development Tools" --skip-brokenTo continue, you must go to the directory:
cd /usr/srcLoading source files
We get the latest version from the Python.org website. Visiting it, under "Downloads\Source code" copy the download link we found and need. Then run in the terminal, pasting in the just copied link:
Python source files are downloaded from the official website maintained by the Python Software Foundation. Using the official source ensures that you receive a secure, stable, and up-to-date Python release without modifications, which is especially important for production and server environments.
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.11.3/Python-3.11.3.tgzAfter downloading, you must retrieve the contents of the archive. You can use this command to do so:
tar xzf Python-3.11.3.tgz
Navigate to the resulting Python-3.11.3 folder and install directly from the source code:
./configureComplete the installation by executing the commands one after the other:
makemake installMake sure the update is successful by sending a line to the terminal:
python3 --versionIf version 3.11.x of Python is displayed, then all previous steps have gone correctly! It is now possible to use the universal programming language for your own purposes.
Python version update
If you already have an earlier version of Python, follow the steps below.
Installing additional Python packages
In order to perform a Python version upgrade, a few new packages must be supplied in addition. Send commands to the terminal:
yum groupinstall -y "Development Tools" --skip-brokenwget https://public-yum.oracle.com/public-yum-ol6.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/public-yum-ol6.repo
dnf --enablerepo=powertools install libpcap-devel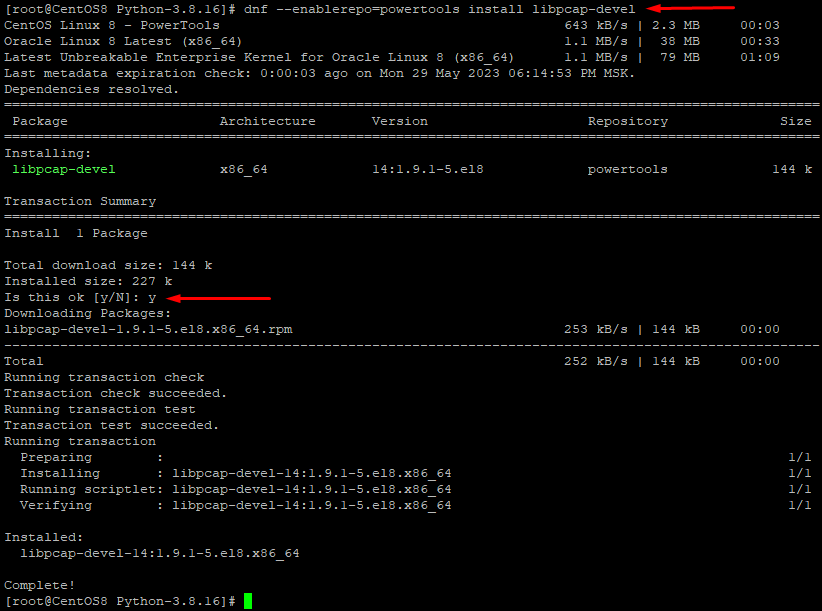
sudo dnf install zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel libffi-devel 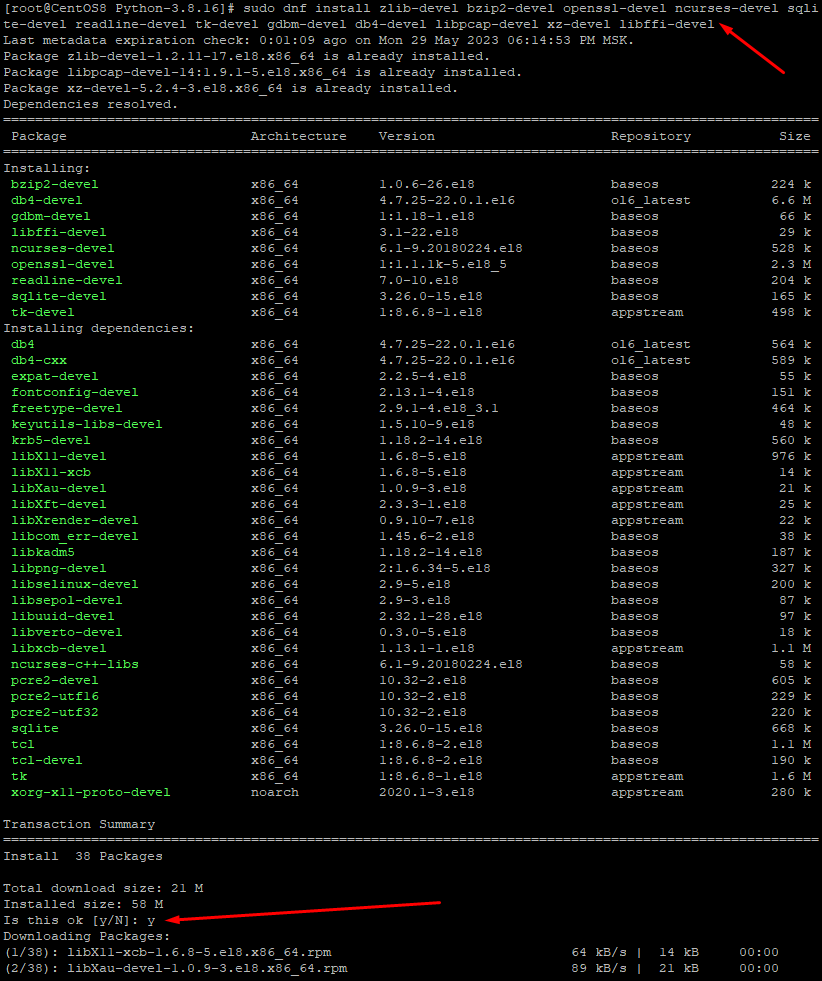
Loading source files
We get the latest version from the Python.org website. Visiting it, under "Downloads\Source code" copy the download link we found and need. Then run in the terminal, pasting in the just copied link:
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.11.3/Python-3.11.3.tgzAfter downloading, you must retrieve the contents of the archive. You can use this command to do so:
tar xzf Python-3.11.3.tgz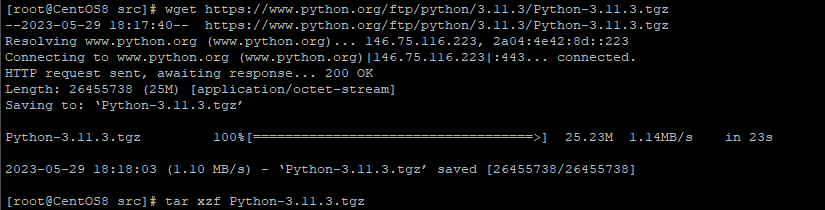
Update version
Navigate to the resulting Python-3.11.3 folder and install directly from the source code:
./configure --enable-optimizationsmakemake installCheck update
Make sure the update is successful by running the command:
python3 --version![]()
If Python version 3.11.x is displayed then the update was successful.
Summary
In this review, we looked at "How to update Python on CentOS" by using source code files.
You may be interested in the following materials on the subject
FAQ: Installing and Upgrading Python on CentOS
- Q: Why should I upgrade to the latest version of Python on CentOS?
A: The latest Python releases bring important security patches, performance improvements, and new features that older versions lack. Upgrading ensures your applications run securely and efficiently. - Q: Can I install multiple Python versions on CentOS?
A: Yes. You can compile a new version from source and keep it alongside the system default Python without breaking dependencies. Just make sure to call the correct version (e.g., python3.11). - Q: What if I already have Python installed—should I remove the old version first?
A: No. CentOS relies on Python for system tools, so do not remove the default version. Instead, install the latest version in parallel. - Q: What packages are required before compiling Python from source?
A: You’ll need development tools and libraries such as gcc, zlib-devel, openssl-devel, readline-devel, libffi-devel, and others to ensure a successful build. - Q: How do I verify that Python was installed or upgraded correctly?
A: Run the command python3 --version. If it shows the expected Python 3.11.x release (or higher), the installation/upgrade was successful. - Q: Is it safe to update Python on a CentOS server?
A: Yes, if done correctly. You should never remove the system Python version used by CentOS. Instead, install the latest Python release in parallel using make altinstall and explicitly call the required version (for example, python3.11). This approach prevents breaking system tools and services. - Q: Should I use pyenv instead of compiling Python from source?
A: pyenv is a convenient option for development environments and local machines. However, on production CentOS servers, compiling Python from source provides more control, predictable behavior, and better compatibility with system libraries, making it a preferred approach for server deployments.



