Introduction
Setting up a secure network with modern firewalls and IP tables can present some challenges. Here are a few difficulties you might encounter:
- Complexity: Configuring and managing modern firewalls and IP tables can be complex, especially for users who are not familiar with network security concepts. Understanding the syntax, rules, and policies associated with these tools requires technical expertise and a good understanding of networking protocols;
- Rule Management: Creating and managing firewall rules and IP tables can be challenging, particularly when dealing with a large number of rules or complex network setups. It's crucial to carefully design and maintain rules to ensure proper network security without inadvertently blocking legitimate traffic or leaving vulnerabilities open;
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between modern firewalls, IP tables, and your network infrastructure can be a challenge. Different firewall solutions have different features, syntax, and configurations, which may require additional research or troubleshooting to integrate seamlessly with your specific network environment;
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuous monitoring and maintenance of the firewall and IP tables are essential for maintaining network security. Regularly updating rules, reviewing logs, and analyzing network traffic patterns can be time-consuming but critical for identifying and mitigating potential security risks.
To address these difficulties, it is recommended to have a solid understanding of network security concepts or consult with professionals experienced in network security to help with the setup and management of modern firewalls and IP tables. Additionally, keeping up-to-date with the latest security best practices and seeking out relevant resources or documentation can help navigate the complexities associated with securing your network effectively. In that instructions we provide solution for this newbie user experience and acquaintance with network security.
Requirements
- Root rights;
- Ubuntu 20.04 or higher version;
- Several knowledge about work OS ;
- Internet connection.
Installation
First of all, in that instruction we need to update index of packages and packets on the entire system, due-to our OS may оbsolete:
apt update && apt upgrade -y
After this inventories all interfaces and network connection on you system for making plan. How can we build more securely and safety perimeters of our OS and adjacent network?
Classic scheme represent two main concepts: deny all traffic due to people factor, which explain vulnerabilities and weakness place that we dont fix, and above on that rule allow all legitimate connections and request.
Let's build a plan and configure step-by-step.
Install all needed package for your system via command below:
apt install ufw && sudo ufw status
Confirm installation of the package by pressing Y button. And wait till the end of the all process, then we can start configure our system:
apt install net-tools -y && ip a 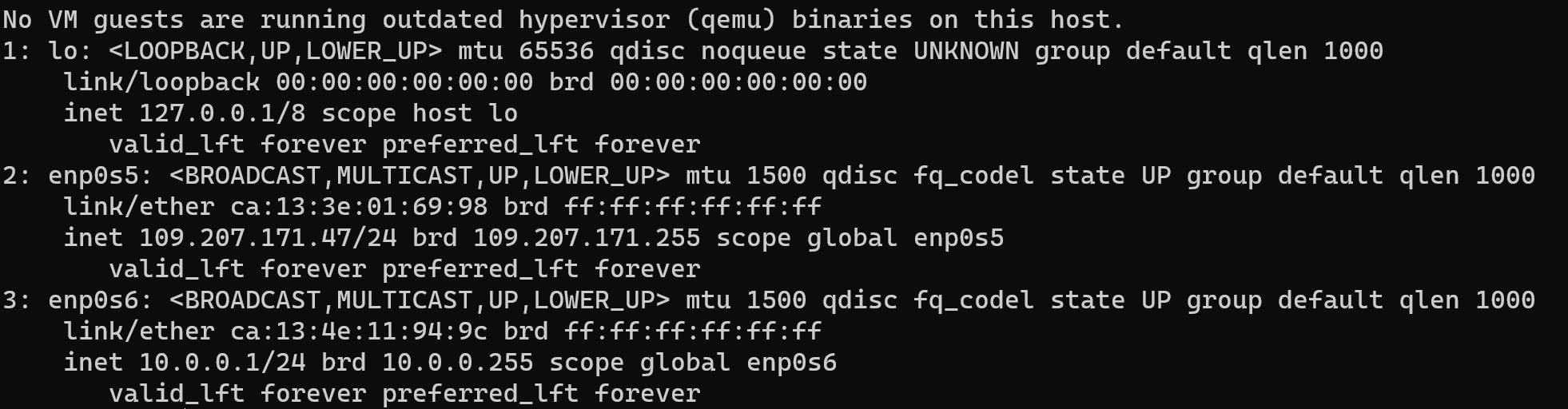
On the screen above we can see all interfaces our system that required to be on protect with rules UFW or uncomplicated firewall.
Configure and protect network
We have internal — enp0s5 and external — enp0s6 networks. Before we will add some rules, theory: each new raw with conditions have more high priority then previous rules. For example, we add deny rule for all interface and then allow one type protocol connection. That will added and we get as the result network with denied connections at all, with one type of protocol exception.
Let's DENY all traffic via command below:
sudo ufw enablesudo ufw default deny incoming && sudo ufw default deny outgoingFor set up rules at the beginning we turn on utility and set rules for default settings to all interfaces.
Then for local process we need to allow internal traffic between main components of OS:
sudo ufw allow from 127.0.0.1 && sudo ufw allow from 10.0.0.0/24
You need to indicate your self IP's range for internal network, that help to processing all traffic from device in that area.
Next we allow outgoing traffic from machine and deny incoming from WAN:
sudo ufw default allow outgoing 
Allow ping's traffic via SSH protocol:
ufw allow 22/tcp 
Allow DNS connection:
ufw allow 53 
Allow HTTP and HTTPS connection for user purposes:
ufw allow 80 && ufw allow 443 
Check all traffic via testing command:
ufw deny in 80 && curl -p 80 google.com 
As you can see all rules have a permission to block incoming and outgoing traffic. For delete this rules enter:
ufw delete deny in 80 
That's minimal configuration for your server, which can protect from illegitimate traffic that come from WAN.
Shutdown rules
If you have reason for turn off firewall you can use reset or disable action on ufw utility:
ufw reset
And you can also turn off all software with command:
ufw disable
For full uninstallation software you can use command:
apt purge ufw
Conclusion
Setting up a secure network with modern firewalls and IP tables can be complex and challenging, especially for users who are not familiar with network security concepts. It requires understanding the syntax, rules, and policies associated with these tools, as well as ensuring compatibility with the network infrastructure. Continuous monitoring and maintenance are crucial for maintaining network security and mitigating potential risks.
To address these difficulties, it is recommended to have a solid understanding of network security concepts or seek assistance from professionals experienced in network security. Staying up-to-date with the latest security best practices and utilizing relevant resources and documentation can help navigate the complexities of securing your network effectively.
The provided instructions offer a solution for newcomers to gain experience and familiarity with network security. By updating the system, installing necessary packages, and configuring UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) step-by-step, users can establish a secure network. The instructions cover concepts such as denying all traffic, allowing specific protocols and connections, and implementing rules for both incoming and outgoing traffic. The importance of protecting internal and external interfaces is emphasized, along with the flexibility to enable or disable the firewall as needed.



