Introduction
Communicate with operation system divide into two types GUI and CLI, over the core users install various of shell for more comfortable experience. But no one of this type have a top position due to specific of purpose using OS. Newby users prefer graphical interface that more intuitive and user—friendly un compare with command line. There is Gnome, KDE, Cinnamon, MATE, etc. All of that have bundle and kit of utilities and graphical elements for different purposes: office work, programming, gaming, web—surfing and more. CLI on another hand suggest different kind of pleasure and comfort for administrators, developers and any IT—specialist who need to use Ubuntu due to advantages.
Simplification The terminal (or command line) and the graphical user interface (GUI) represent two different ways of interacting with the operating system. Each of them has its advantages in different situations. Here are a few advantages of the terminal over the GUI:
- Speed and efficiency: In the terminal, you can execute commands using text commands. This can be much faster and more efficient than searching and clicking on menus and buttons in the GUI. When you know the commands, it can save a lot of time;
- Flexibility and control: The terminal provides more control over the system than the GUI. You can perform complex operations, automate tasks using scripts and configure the system more precisely;
- Remote management: The terminal allows you to manage remote systems via SSH or other protocols, which is especially convenient for the administration of servers and remote computers;
- No dependence on the graphical shell: In some situations, for example, when working with servers where there is no graphical shell, the terminal becomes the only available way to interact with the system;
- Convenience for experienced users: For experienced users and administrators, the terminal can be a more convenient tool for performing complex tasks, especially if they are familiar with commands and scripts.
However, GUI also has its advantages, especially for beginners and those who prefer visual interaction. The GUI provides a more intuitive and visual way to access functions and applications, making it more accessible to a wide range of users.
So, using a terminal or GUI depends on your preferences, level of experience and specific tasks that you perform on a computer or server. In most cases, the combination of using the terminal and GUI allows you to achieve the best result and efficiency in working with the operating system.
Terminal from Windows
You can open terminal in Ubuntu by create connections in your another machine, for example you can use Windows terminal — PowerShell for remote manage the system. In the windows you need to press combination of button Win + X and you will see pop—up menu:
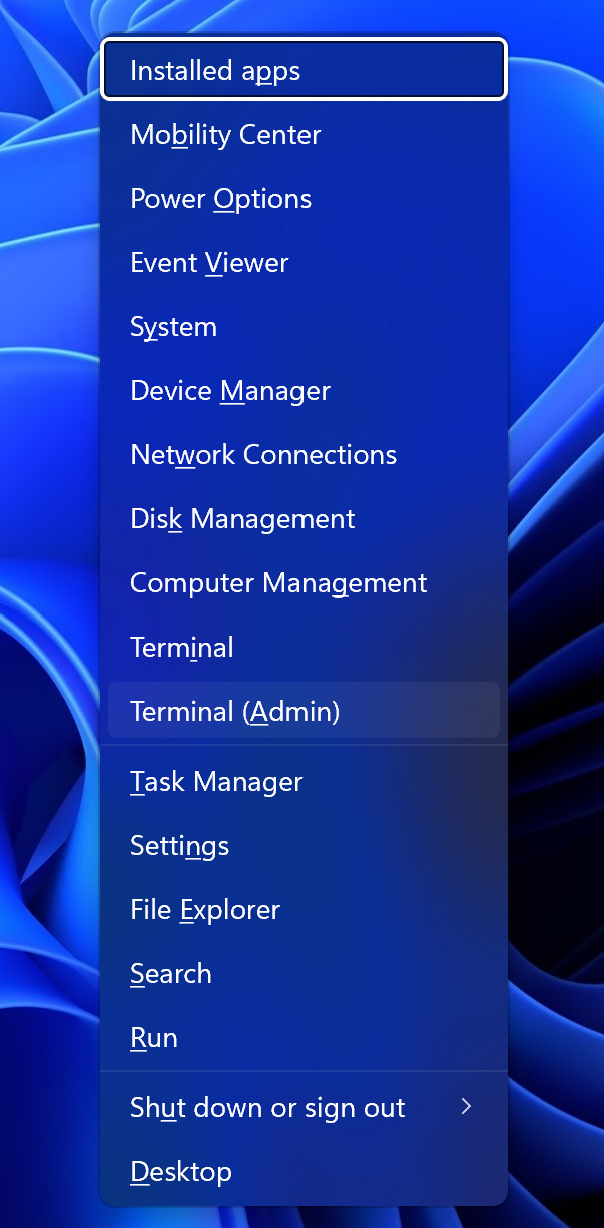
In that list you need to choose Terminal(Admin) and you will see open window. Type command below that connect to the server and use Ubuntu terminal, but remember, you need to change IP—address to your machine's IP:
ssh root@93.183.72.17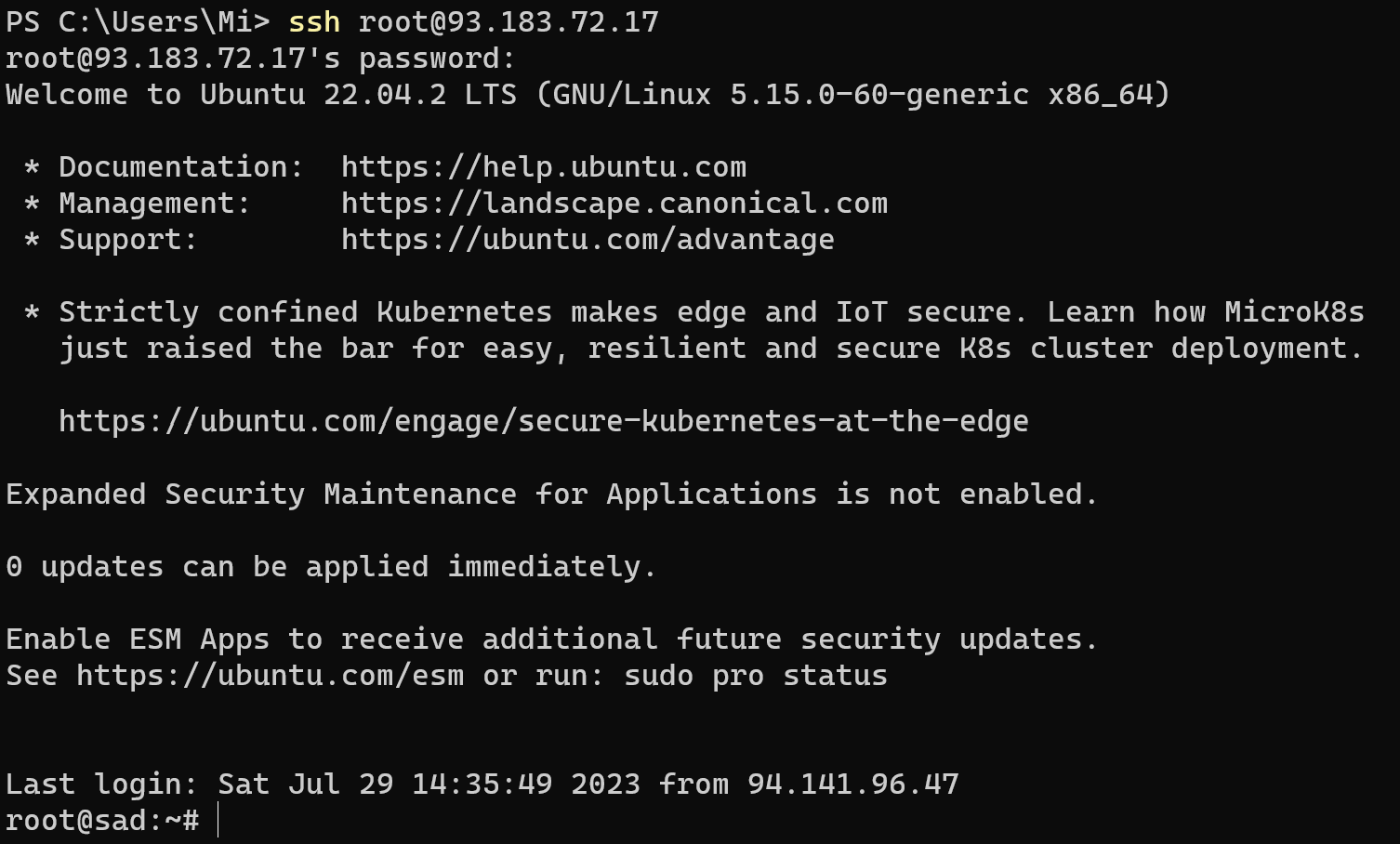
After you input your credentials, you will get access to the system!
GUI methods
If you have straight access to GUI interface you can press combination of button Ctrl + Alt + T and you will see displayed window of terminal in the system:
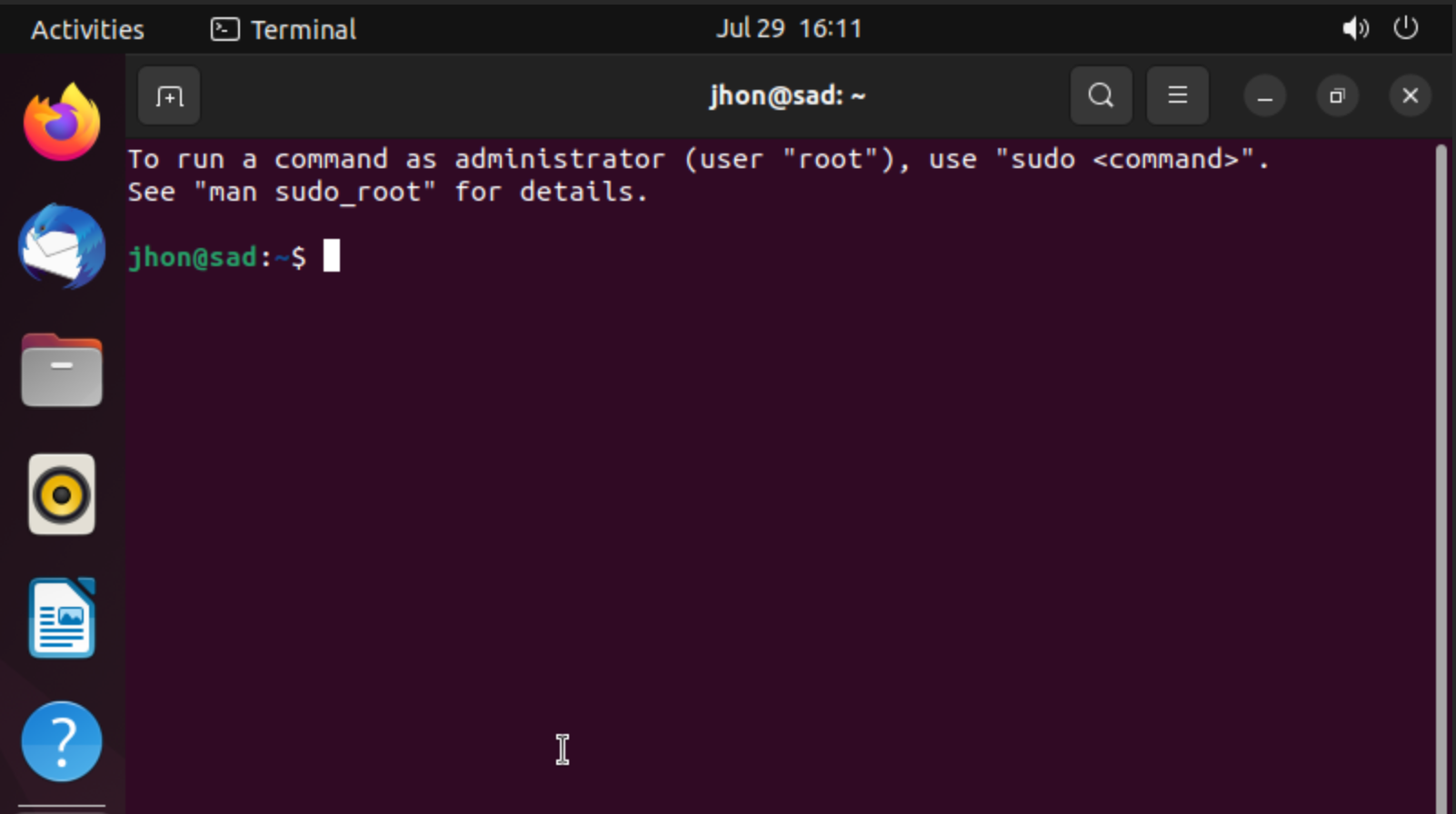
But if you don't preferee that combination and that you seem obstacle, you can can change in the settings bundle of button and allocate needed combination. Click button on the bottom corner and type in the search bar Settings next scroll left bar until you see Keyboard then scroll right bar to the point Keyboard Shortcuts. After that click on the button under the title and choose Launchers and change combination by clicking needed button:
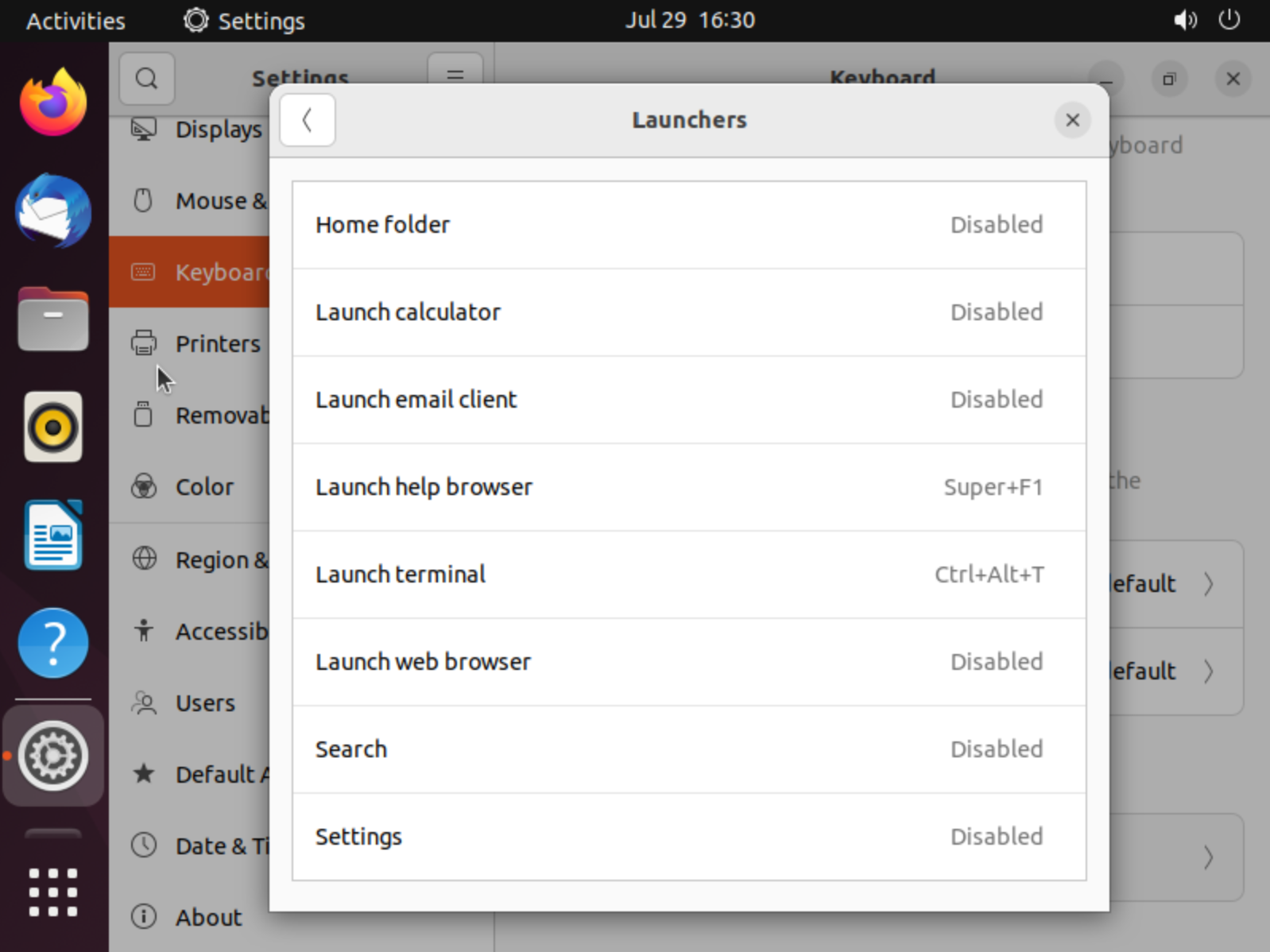
Also you can press combination of button Alt+F2, windows pop up and for Gnome GUI you can enter:
gnome-terminal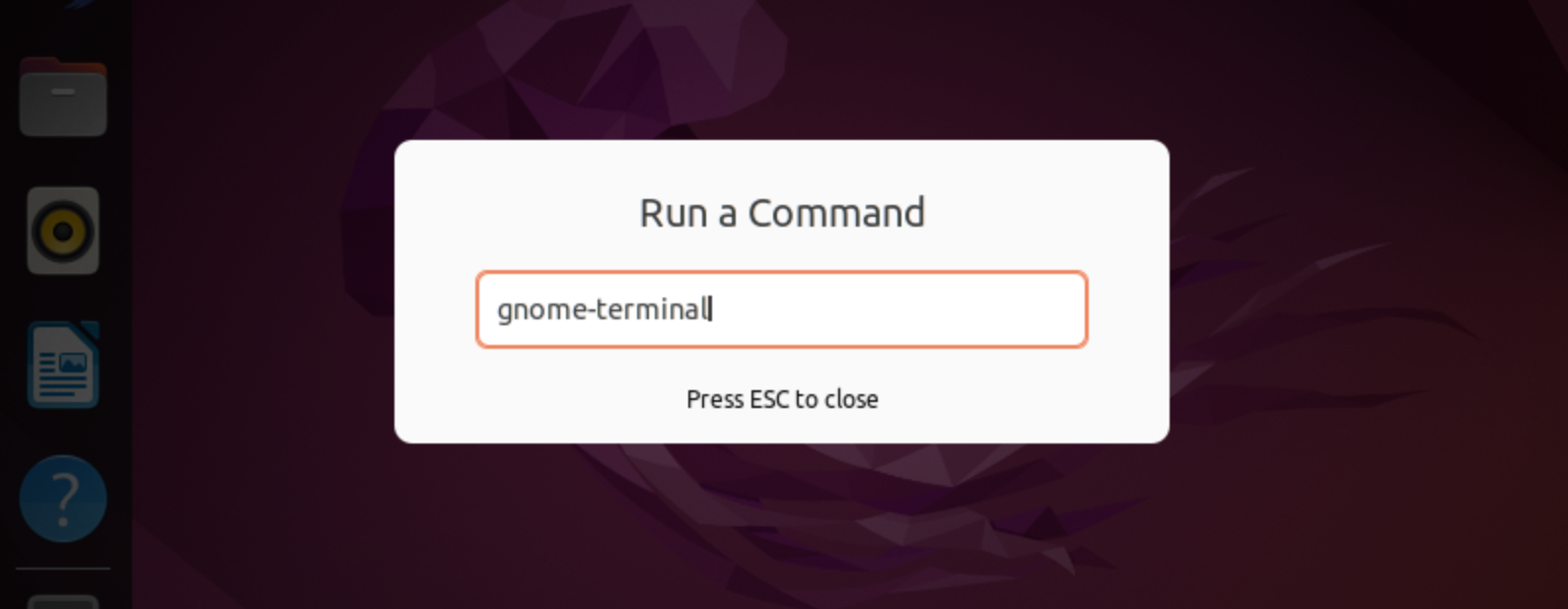
And you will see open windows with them! Open search bar and type Terminal for open window:
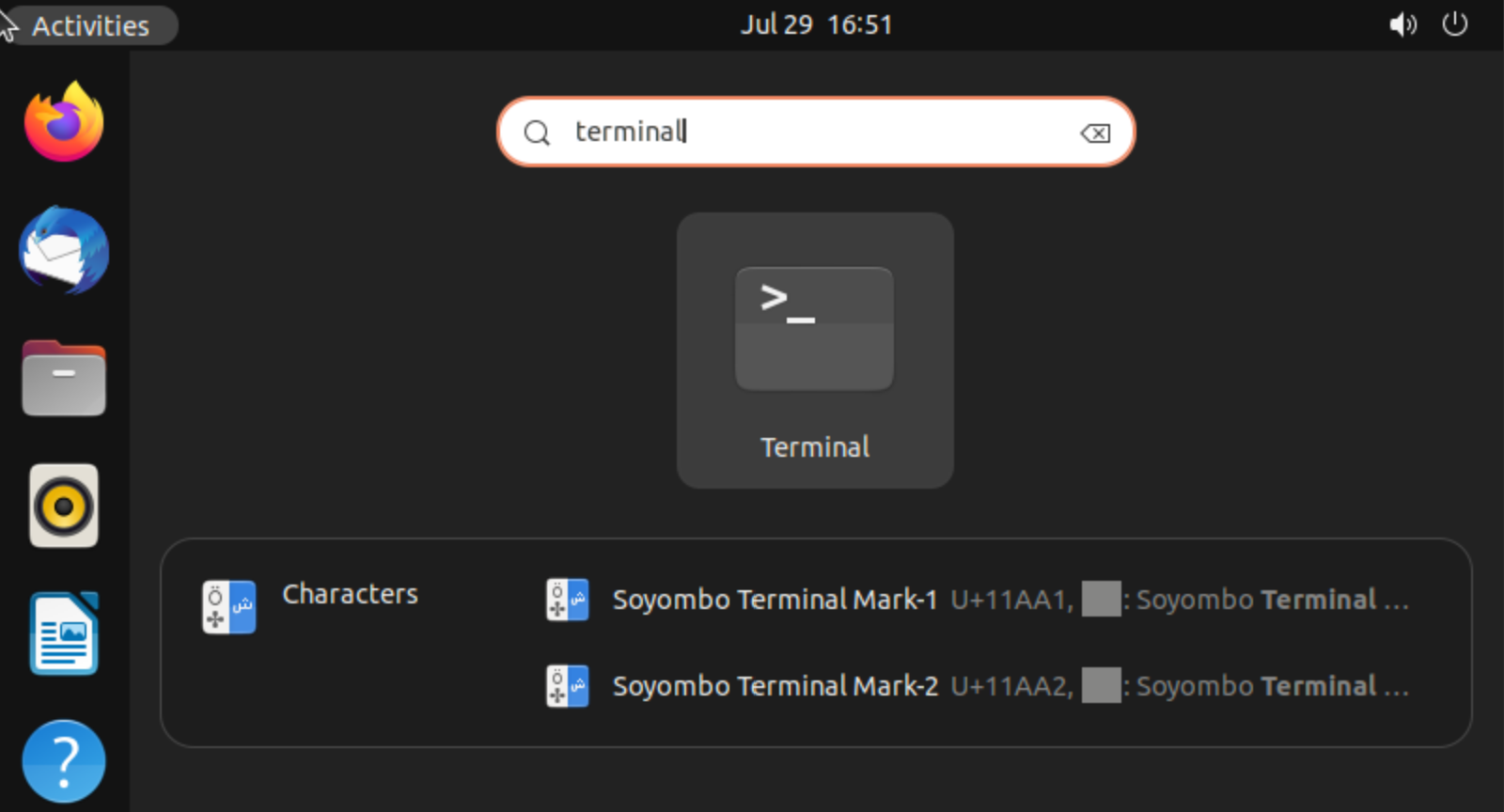
Conclusion
The communicating with an operating system can be achieved through two main types of interfaces — the Graphical User Interface (GUI) and the Command Line Interface (CLI). Each of these interfaces has its advantages and serves specific purposes.
The CLI, or terminal, offers benefits such as speed, efficiency, flexibility, and remote management capabilities. It is a preferred tool for experienced users, administrators, and IT specialists who require precise control and automation. It also becomes essential in scenarios where graphical shells are not available, like server administration.



