Instructions for configuring Firewall rules for virtual server networks in the control panel.
What is a network firewall?
You can control access to the public server network, incoming and outgoing data packets directly from the control panel using the firewall. This option is not charged separately and is included in the network price.
At the moment there is a limit of 50 rules. If it is not enough for you, you can increase it by submitting a request to Technical Support.
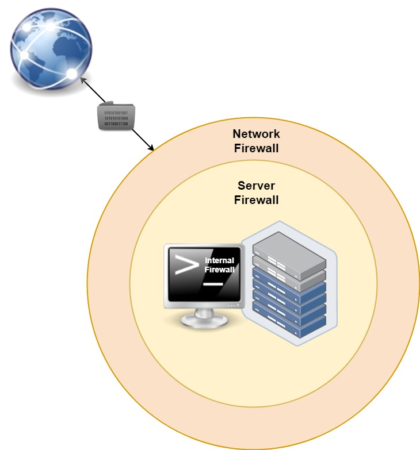
Network Architecture
It is necessary to understand the order of operation of existing firewalls in order to avoid the firewall rule conflict and to ensure correct firewall configuration. First, you can configure the firewall for the private network. Secondly, you can configure the firewall for the server through the control panel. Thirdly, you can configure a back-end firewall, for example, for Linux via iptables; As for Windows, the firewall is built-in.
Incoming packets will be handled first by a network level firewall (if any). If the packet has passed, the firewall at the server level will be applied further, the last one will be the internal software mechanism. As for outgoing packets, the reverse sequence of actions will be applied:
Creation of rules
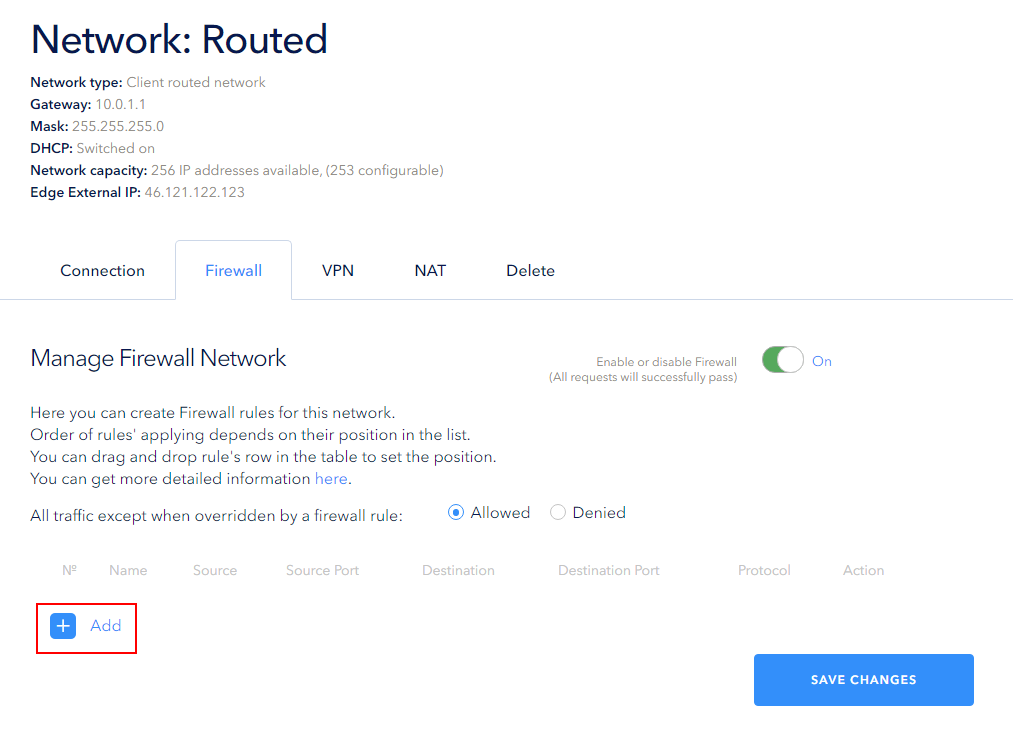
The firewall configuration is available for networks and can be found in the network settings of the Firewall section.
Important:
— the order of the rules matters: the smaller the order number of the rule (the higher it is in the list), the higher its priority. You can change the order of rules with Drag and Drop by dragging the rule with the left mouse button to the desired position;
— off - all data packets, both incoming and outgoing, pass through the router.
Packets not covered by any rule can be allowed or denied; they are allowed by default.
Click the Add button to create a rule:
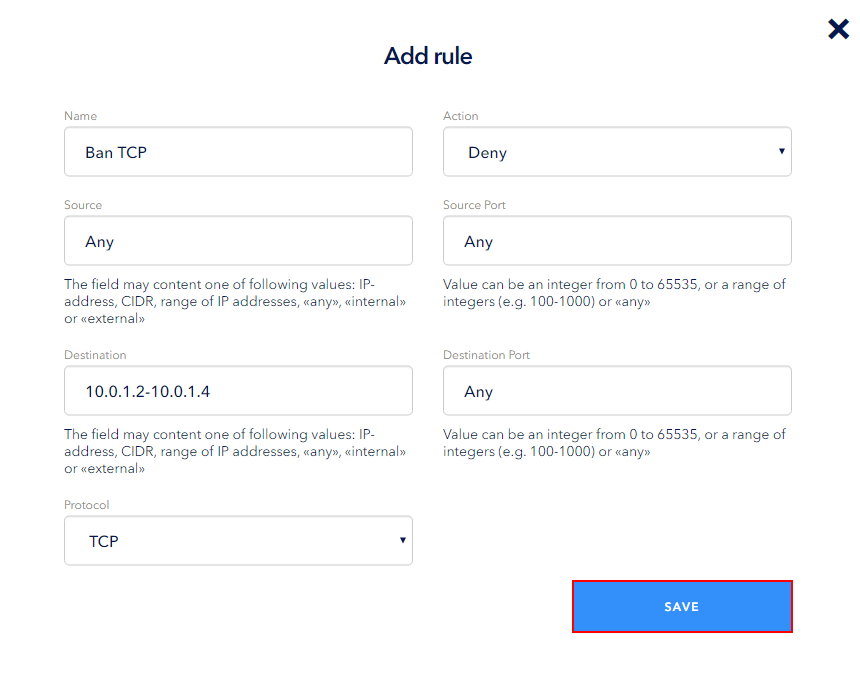
It will open the window for adding a rule. The following fields should be filled in:
- Name is a user friendly name (not more than 50 characters), which usually briefly describes the purpose of the rule;
- Action is an action to be applied that takes one of two values: Allow or Deny. Allow means that the data packets are allowed to be sent, Deny means that the data packets are not allowed to be sent;
- Source/Destination — specify the server IP address or one of the values: IP address, CIDR, IP address range, any, internal and external;
- SourcePort/DestinationPort — when selecting TCP, UDP or TCP and UDP, you can specify either a port or a range of ports or 'any';
- Protocol is a type of protocol. ANY, TCP, UDP, TCP and UDP and ICMP are available.
Click Save to create a rule.
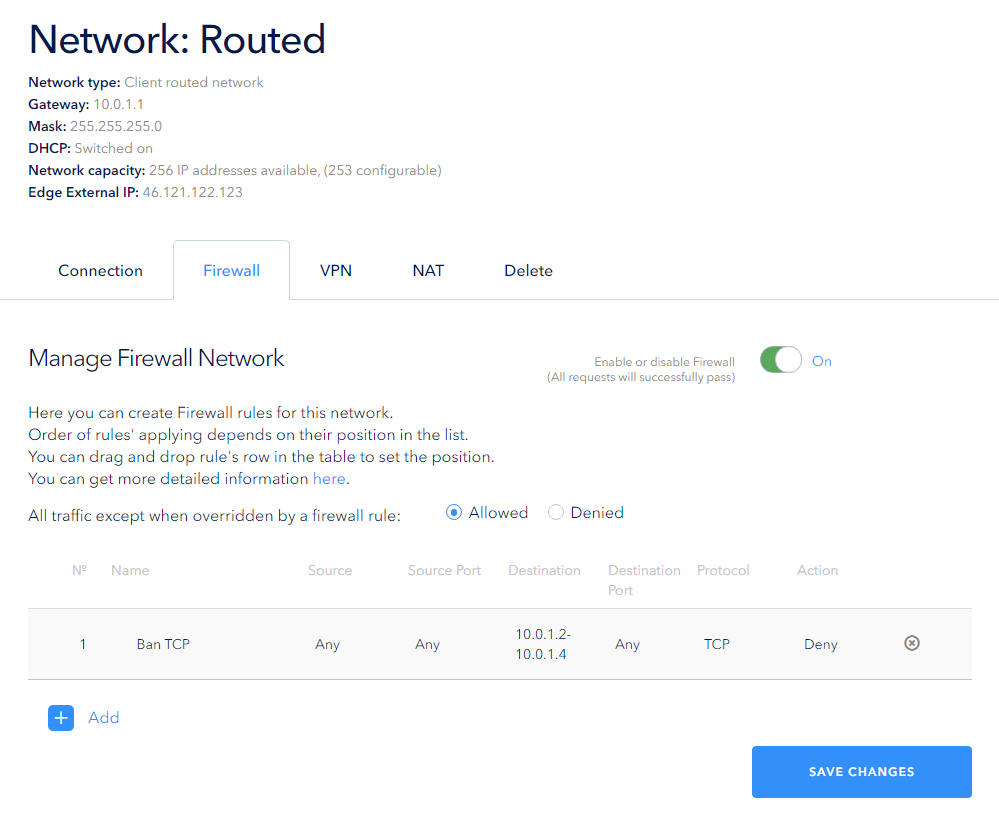
In our example, the rule blocks incoming Tcp packets for the address range 10.0.1.2-10.0.1.4:
In order for the rule to take effect, you should save your changes by clicking the Save button. You can create several rules and then save them all at once:
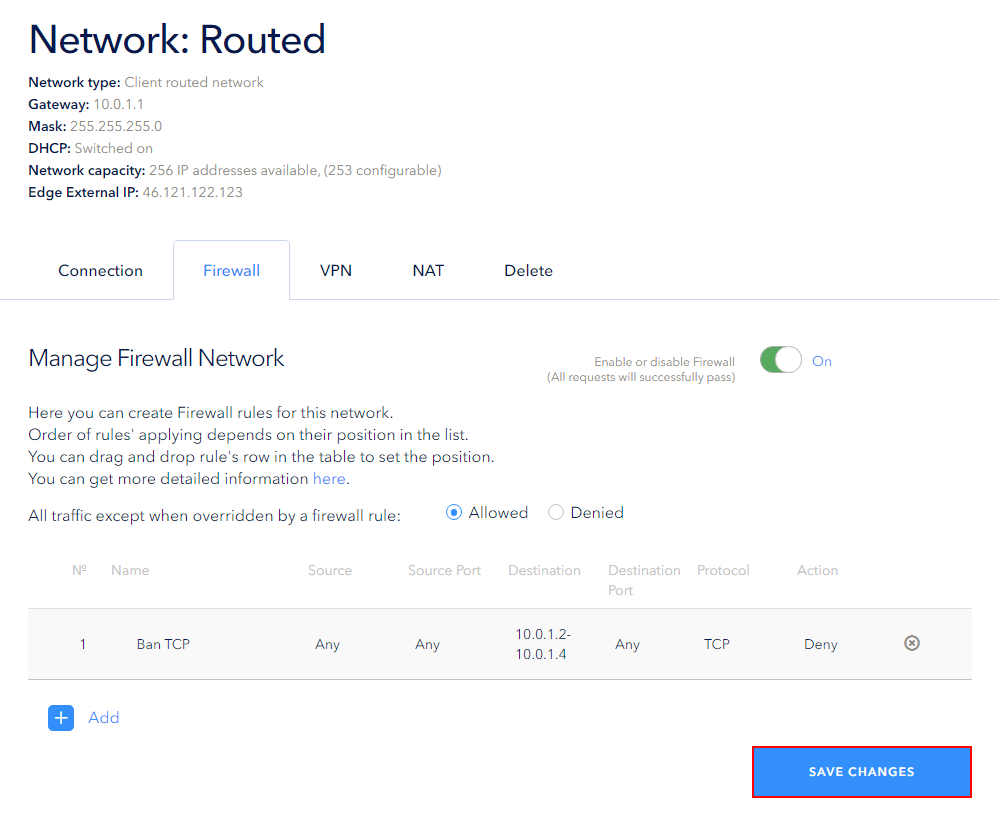
After that, the page will look like this:
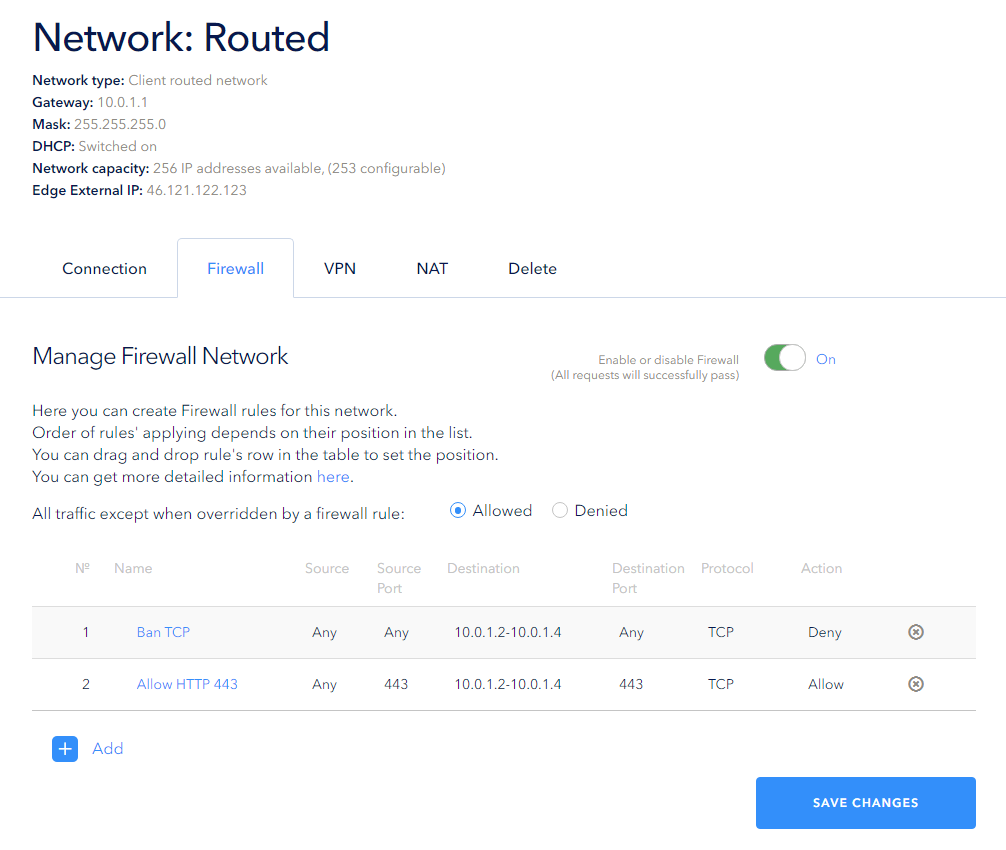
Example of rule priority setting
The smaller the order number of the rule (the higher it is in the list), the higher its priority. For example, after creating a Deny rule for incoming Tcp packets for a specific address range, let's create a rule that allows incoming packets to be received on Tcp port 443 from outgoing port 443. Once the changes are saved in this configuration, this port will still be unavailable because the Deny rule has higher priority:
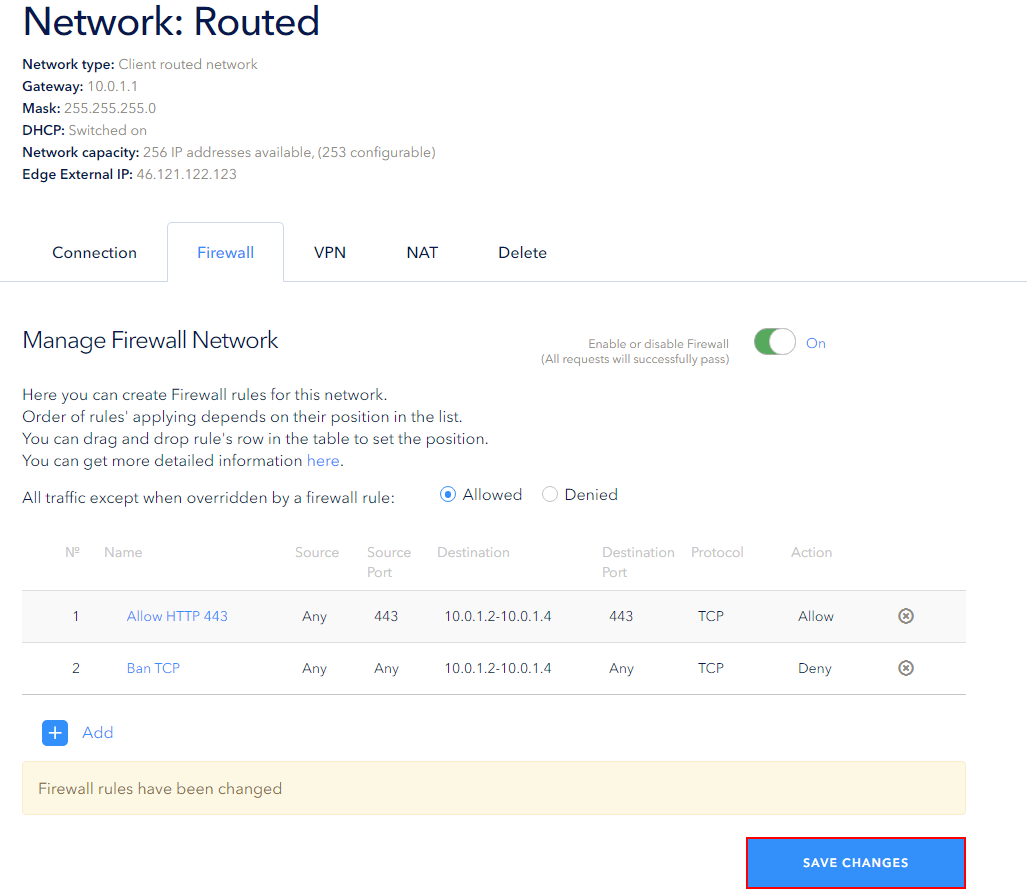
Drag and drop the Allow rule to the first place using the left mouse button to change the priority of the rules, then save the changes:
The order numbers of the rules will be changed after they are saved, and their priority will also be changed:
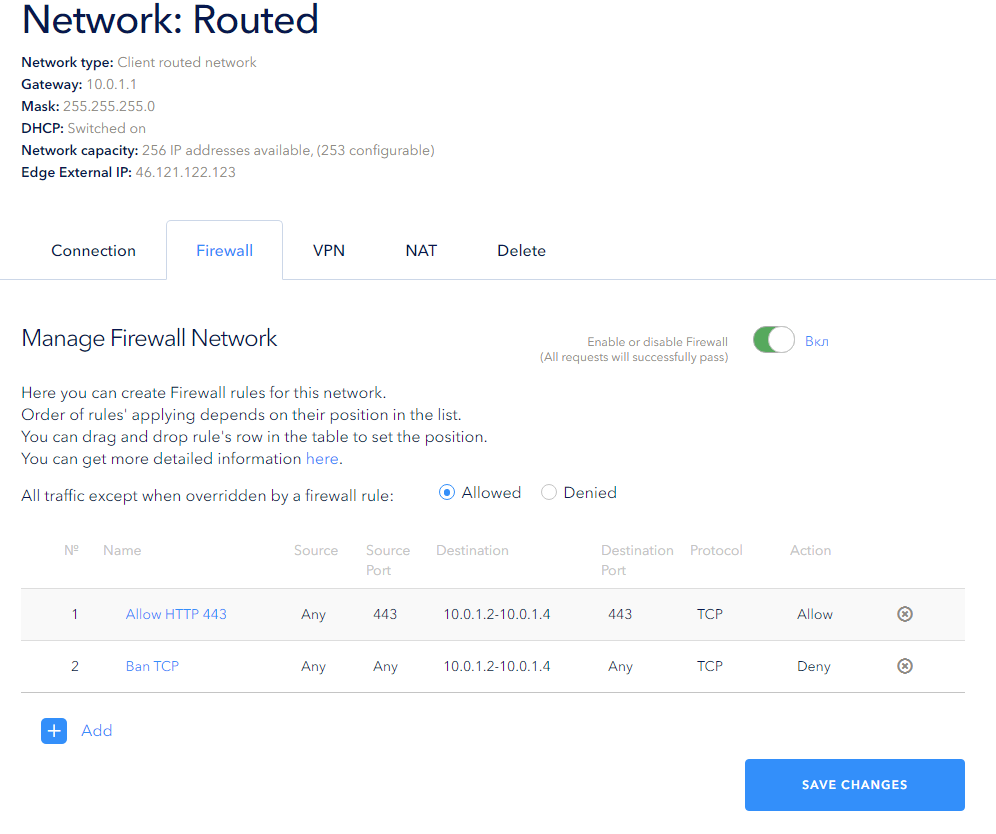
Now the firewall configuration allows Tcp packets to be passed through Tcp port 443 to the network on a certain range of addresses, other Tcp packets will not pass through. All other packets that are not covered by the rules will pass into the network.



