Intro
Samba is a powerful open-source solution for file and print sharing that implements the SMB/CIFS protocol, originally developed by Microsoft for Windows systems. It enables seamless file sharing between Linux and Windows machines within the same network.
In addition to basic file sharing, Samba supports user authentication, access control, printer sharing, and integration with Windows environments. In this beginner-friendly guide, you’ll learn how to install and configure Samba on Debian, create users, set up shared folders, and verify access from Linux and Windows clients.
Installing Samba on Debian
First, update the package index and install the Samba package on your Debian system.
sudo apt updatesudo apt install samba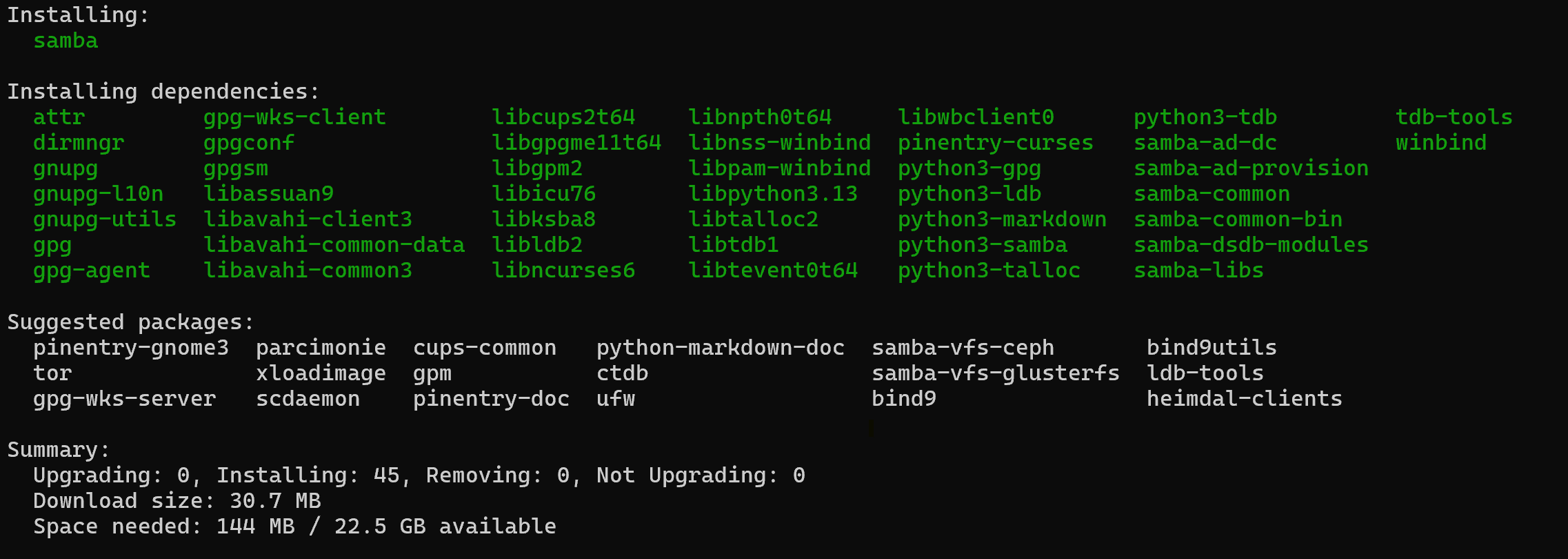
The command above will install necessary packages with their dependencies.
Manage Users
After the installation is complete, create a system user who will have access to the shared resources.Do it:
sudo useradd -m user1Change "user1" with the actual username
Upon completion of the creation process, we should create a password:
sudo passwd user1And then assign the Samba group:
sudo smbpasswd -a user1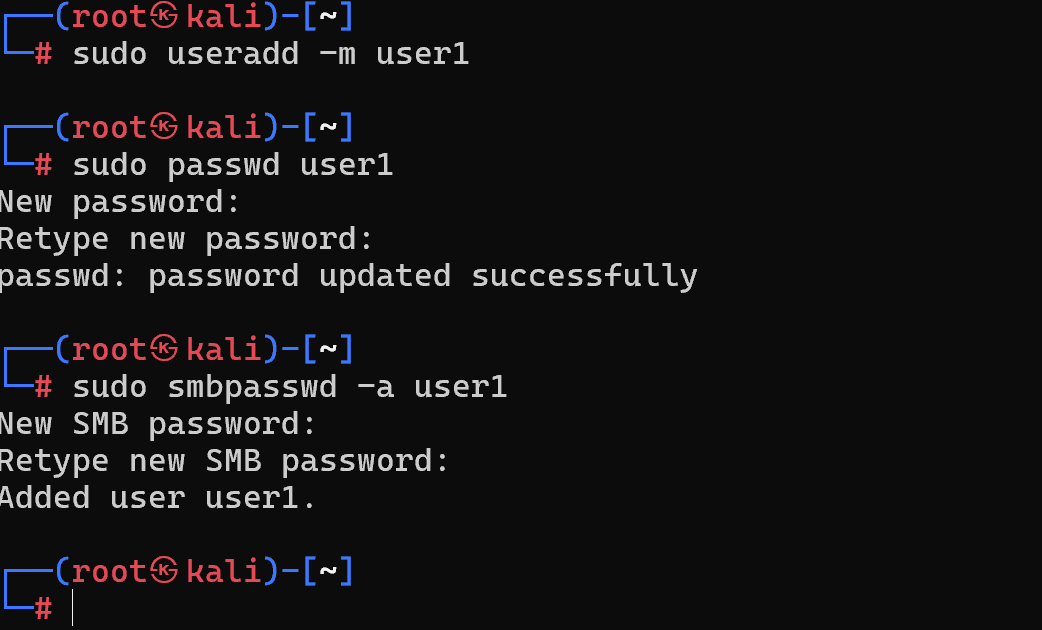
Preparing Shared Directories
After creating and configuring users, we create shares to which they will have access. Create a folder share1 along the path / media
sudo mkdir /media/share1Next, edit the Samba configuration file with a text editor, in this case nano:
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.confIt is used for creation shared folders, grant access to them, and other important service settings.
Now make new resource and define access rights to it.
Make a folder "share1", set permissions for user1:
[share1]
path = /media/share1
read only = no
guest ok = no
valid users = user1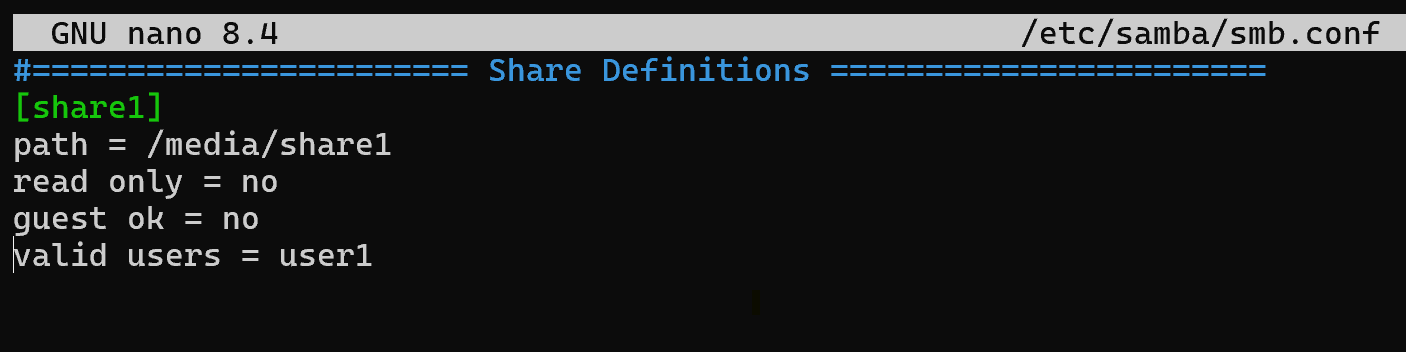
After making these, directory "share1" will be accessible for user1.
Restart Samba
After changing the settings, the service should be restarted:
sudo systemctl restart smbd.service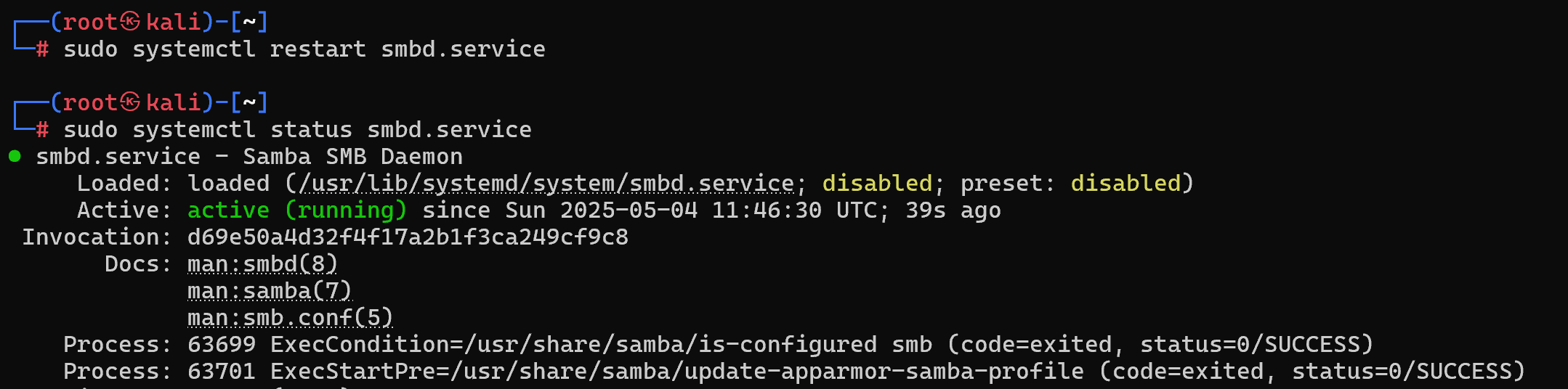
This command will restart the Samba service and commit any changes made to the configuration.
Availability check
Once configured, you can test access to shared folders from another host on the network. To check from the server itself, you can use the smbclient utility, which should first be installed:
sudo apt install smbclient -yFind your server’s IP address with command:
ip a And then verify:
smbclient -U user1 //SERVER_IP/share1 -c 'ls'Or by opening the file manager on another computer and typing in the address bar:
\\Debian_server_IP\share1"Debian_server_IP" is the IP address of the newly configured server.
If everything was done correctly, then as a result you should see the contents of the "share1" folder. In the Windows you can use Explore.exe which have handler for SMB communications:
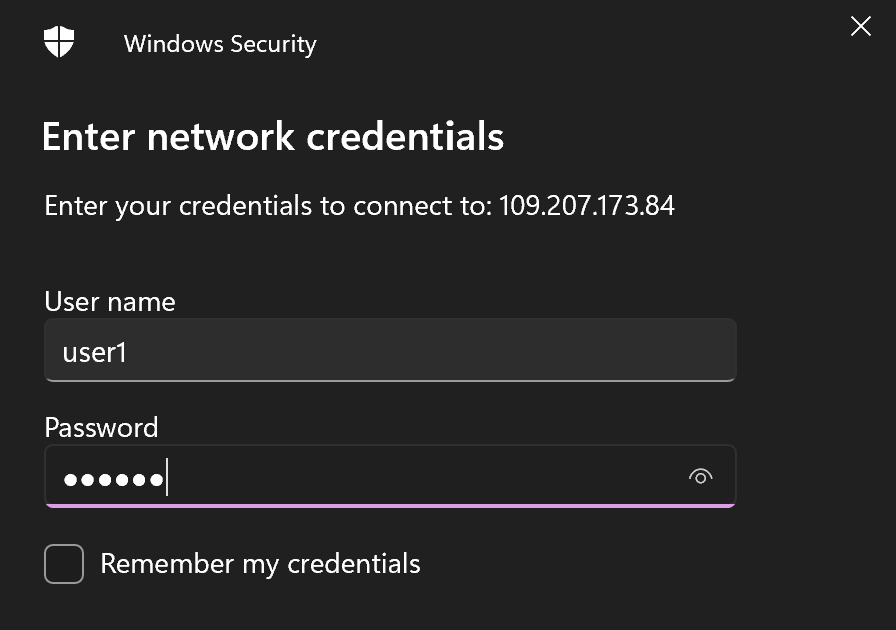
Alright, after that we can use our shared folder under authenticated user1. For more control of user's action you can configure attributes for each! That solution also will be suitable for other distributives like alt Linux with Samba.
Security & Best Practices
- Security and Best Practices
- Use strong passwords for Samba users
- Avoid using guest access on production systems
- Restrict access using valid users in smb.conf
- Set correct Linux file permissions on shared directories
- Keep Samba packages up to date
You may be also interested in
FAQ
- Q: Do I need to open any ports on the firewall for Samba?
A: Yes. For Samba to work properly, make sure that ports 137, 138 (UDP) and 139, 445 (TCP) are open, especially if you have ufw or another firewall enabled on the server. - Q: Why doesn't Windows see my Samba server?
A: Check that both devices are on the same subnet, file sharing is enabled on the Windows machine, and the workgroup name matches in both smb.conf and on the Windows client. - Q: How do I add a second user?
A: Repeat the useradd, passwd, and smbpasswd commands with a different username. Also, add this user to the valid users list in the corresponding share configuration. - Q: How can I make a shared folder read-only?
A: In the share section of smb.conf, set read only = yes and remove any writeable = yes line if present. - Q: Is it possible to make a shared folder accessible without authentication?
A: Yes, set guest ok = yes, public = yes, and ensure map to guest = Bad User is enabled in the global settings of smb.conf. - Q: Where is the Samba configuration file located on Debian?
On Debian-based systems, the main Samba configuration file is located at /etc/samba/smb.conf.
Conclusion
In this guide, we covered how to install and configure Samba on Debian, create users, set up shared directories, and verify access from Linux and Windows systems.
Samba is a reliable and flexible solution for file sharing in home and office networks. With proper user management and access control, it can serve as a secure and efficient Debian file server for cross-platform environments.



