How to Configure NAT for Routed Networks in Control Panel
Description of the NAT configuration procedure for routed networks in the control panel.
What is NAT?
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a technique used to modify IP address and port information in the headers of IP packets as they pass through a router or firewall. Its most common application is to enable multiple devices on a private local network to share a single public IP address. For example, when a device on the internal network sends data to the Internet, NAT replaces its private IP address with the router’s public IP address.
When external systems attempt to respond or initiate connections, they only see the public IP — typically belonging to the router — and not the individual devices behind it. This setup not only conserves public IP addresses but also adds a significant layer of security. Since internal IP addresses are hidden from the outside world, unsolicited inbound traffic is blocked by default. The router can further act as a firewall, allowing only specific traffic to reach internal machines, effectively controlling access and reducing the risk of external attacks.
The main purpose of creating NAT is to overcome the lack of IPv4 addresses. Our infrastructure uses One-to-Many NAT, i.e. one router's external IP address is displayed for multiple local addresses. This is where you can connect large networks to the Internet using only one external IP address.
Creation of rules
First, you need to create a routed network in the control panel and connect virtual servers to it. Only servers from the same data center can be connected to the same network.
Open the NAT tab, when the network is configured. Click the Add button:
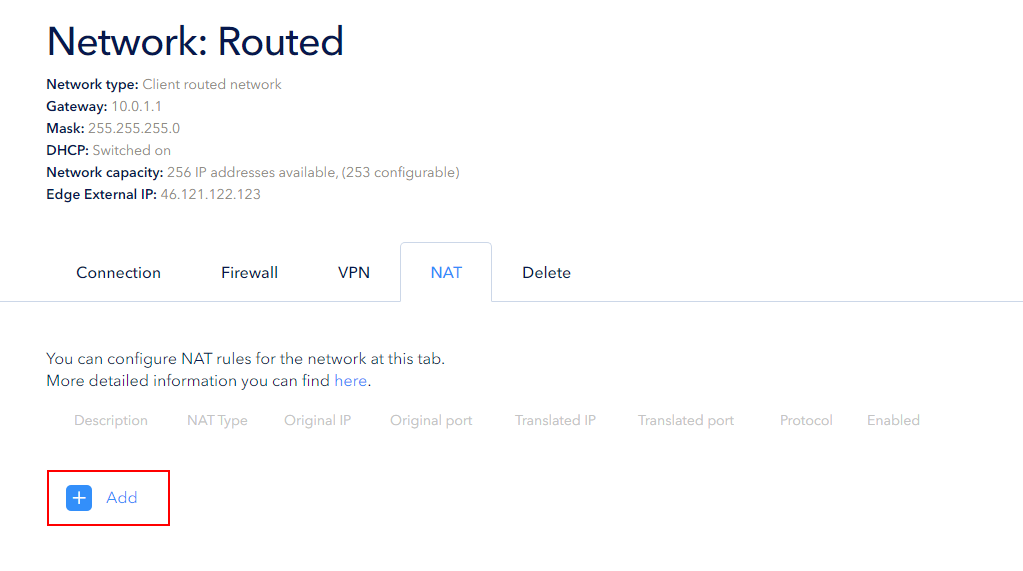
The user can create two types of rules: SNAT or DNAT.
SNAT
SNAT (Source) changes the source IP address of the network packet with the data to another IP address.
Use case: masking and concealing local (private) IP addresses of devices to increase privacy and security.
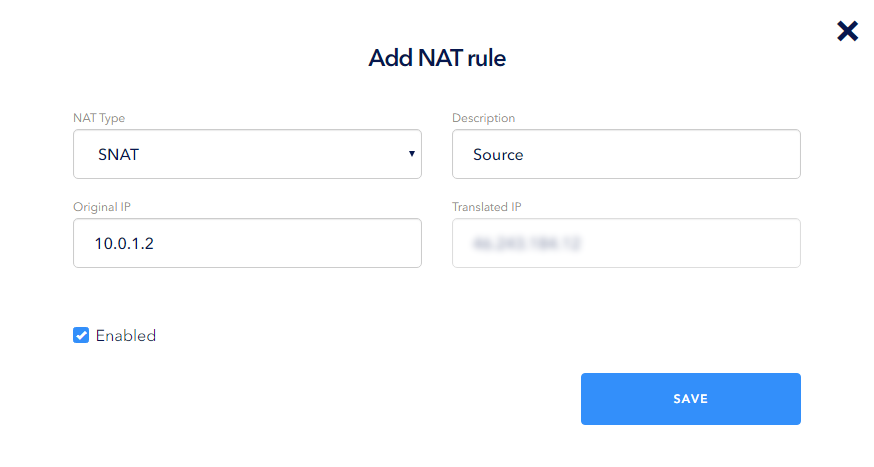
When creating a type rule in the NAT Type drop-down list, select SNAT and fill in the following fields:
- Description is a user-friendly name;
- OriginalIp is a local (private) server address (will be converted);
- TranslatedIp is an external address of the router in the network; this value is entered automatically and cannot be changed.
You can use the Enable check mark to enable or disable a rule:
DNAT
DNAT (Destination) is used to convert the target IP address of a network packet into a different IP address.
Use case: masking internal IP addresses and replacing them with other IP addresses.
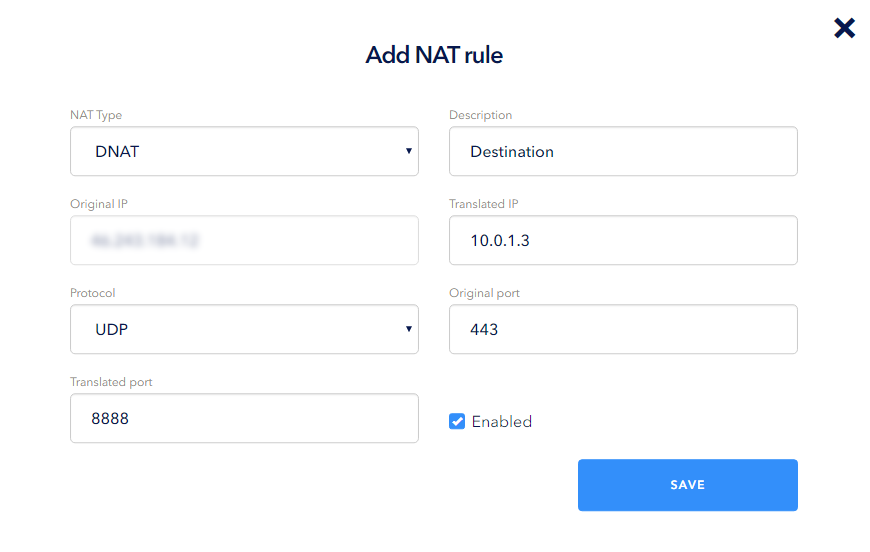
When creating a type rule in the NAT Type drop-down list, select DNAT and fill in the following fields:
- Description is a user-friendly name;
- OriginalIp is an external address of the router in the network; this value is entered automatically and cannot be changed;
- TranslatedIp is a local (private) server address (will be converted);
- Protocol — select the required protocol from the available list of protocols;
- OriginalPort is the port of the router which receives data packets;
- TranslatedPort — is a port of the local server to be changed.
You can use the Enable check mark to enable or disable a rule:
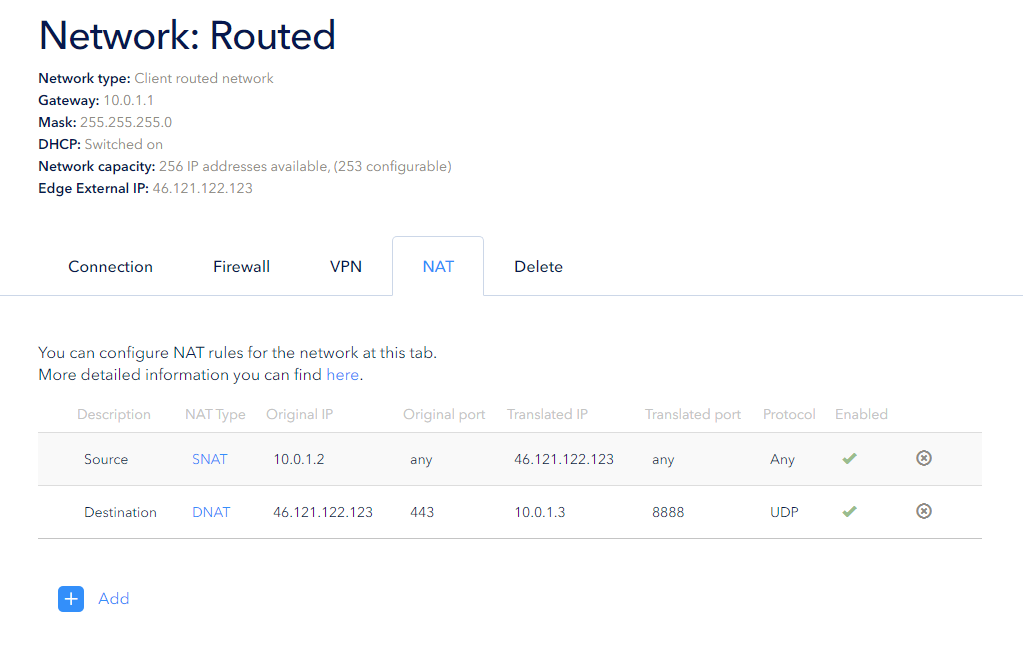
Added rules will appear in the NAT section of the selected network:
Editing NAT rules
The user can edit previously created NAT rules. Left-click on the rule's NAT type field to edit it:
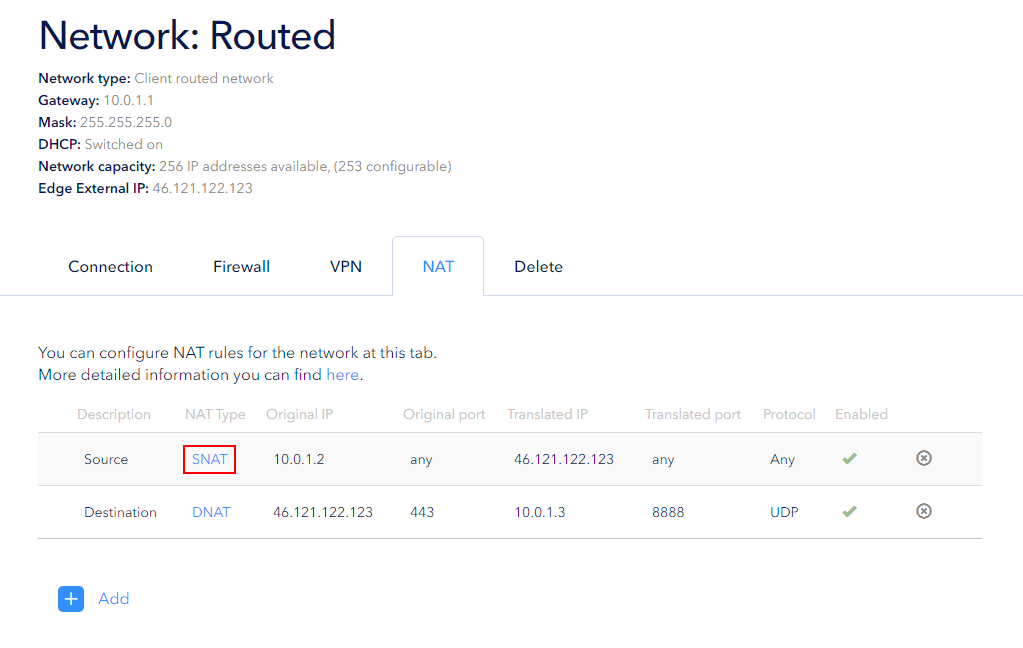
Save the changes.
Note: You can use the Enable check mark to enable or disable a rule.
Deleting NAT rules
If the rule becomes irrelevant, it can be deleted. You can delete it using the Cross button:
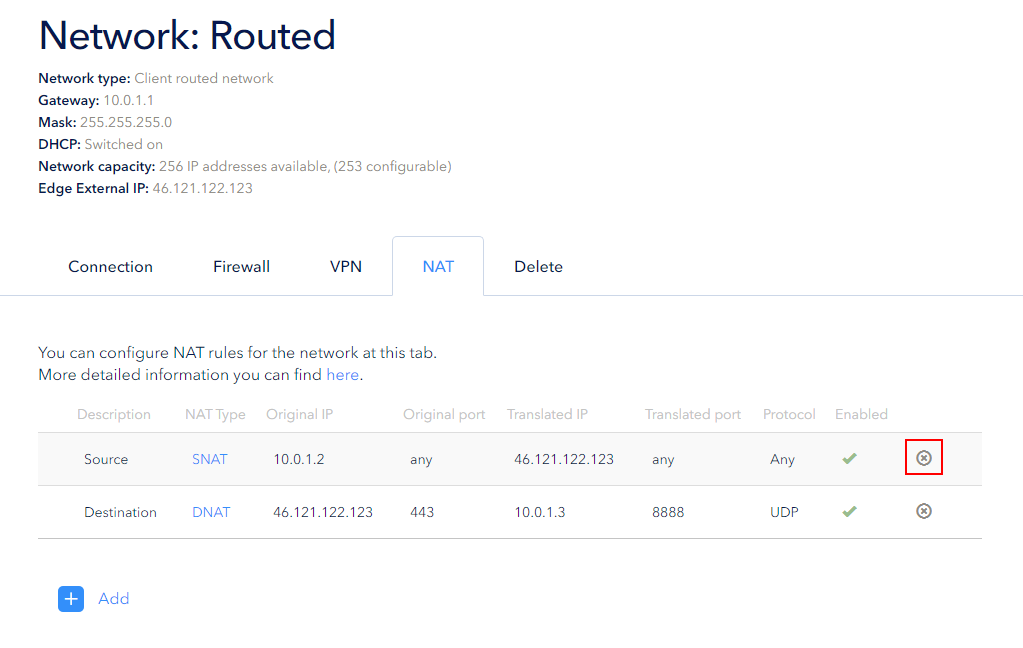
Confirm deleting:

 700
300
700
300
 700
300
700
300
 700
300
700
300


