Why should you use memcached in Centos 7
Each operation system uses much temporary data upon services work. By default, it stores into the special folder on the disk. This method has one negative side - disk read/write operations is so slow even on modern SSD. The best way to avoid this is store temp-files to the RAM, e.g. via memcached.
Requirements
To install caching service and secure it you need to have:
- Server with Linux operation system, e.g. Centos 7
- root access or account with sudo membership
- Optional - iptables or another firewall
Install main package and support tools
Setup is one-line command procedure:
- Authorize on the server and install necessary packages
sudo -s
yum install memcached -y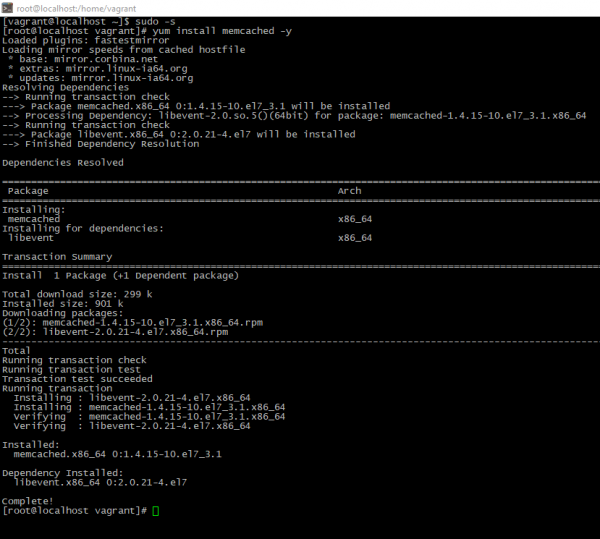
Service configuration
Installed service read its settings from the /etc/sysconfig/memcached file. The most useful flags is:
CACHESIZE # RAM amount, reserved for for caching
PORT # TCP-port which is service-listened
-l # listened IP-address, usually 127.0.0.1 for local connections or "dedicated" address for "external" incoming connections
MAXCONN # allowed simultaneous connections quantity
-S # this option is enables authentication (see further)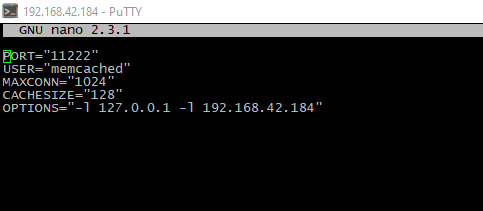
To accept incoming connections please allow them in the firewall settings:
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=<PORT>/tcp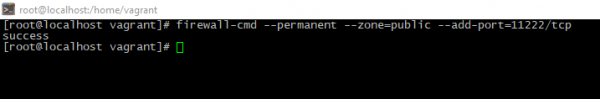
The safety improoving
If your server is accessible from the worldwide, a few security-steps would be nice. Make follow steps to implement simple authentication into memcached:
- Installation command
yum install cyrus-sasl-devel cyrus-sasl-plain -y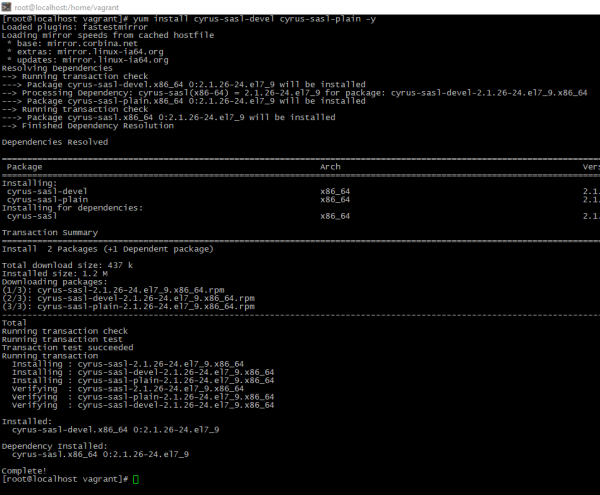
- Create the configuration files:
mkdir -p /etc/sasl; nano /etc/sasl/memcached.conf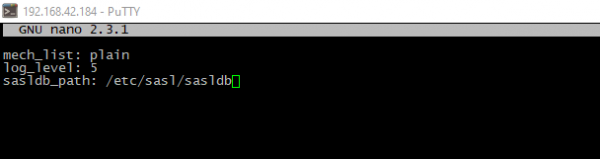
- Then you should fix file permissions and add the "separated" user account for authorization:
saslpasswd2 -a memcached -c -f /etc/sasl/sasldb <MEMCACHED_USERNAME>
chown memcached:memcached /etc/sasl/sasldb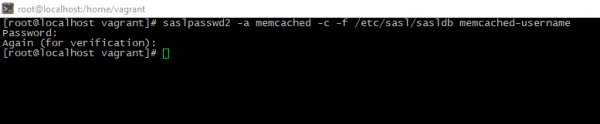
- Next step is enabling authentication in memcache configuration. Just add -S flag
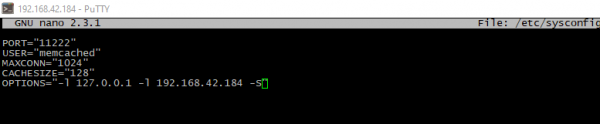
- To apply the settings service should be restarted:
service memcached restartChecking the result
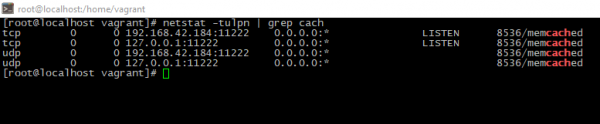
You can simply check is caching service run or not. Just run:
netstat -tulpn | grep cachYou should see something like this
Summary
This instruction said you why you should use caching, how to install and use this.




