Project management in IT: Agile, Scrum, Kanban, Waterfall
Effective project management in IT is one of the key factors determining a company's success in the market, as well as its ability to adapt to changing requirements and technological innovations.
In this article, we will explore the tools and methodologies that serve as the foundation for successful IT business management. Approaches such as Waterfall and Agile will be examined, along with IT management processes. We will also delve into the nuances of applying various tools and methodologies depending on the type of IT project, its scale, and its specifics.
What is IT project management?
Project management is the process of planning, coordinating, organizing, and controlling the execution of projects related to information technology (IT). The primary goal of project management is to ensure the successful completion of projects and the achievement of set objectives.
IT project management takes into account the unique characteristics of information technology and the specifics of software development, which requires a flexible approach to planning and control.
Managing an IT company allows you to:
- Define clear project goals and objectives.
- Develop an action plan to achieve these goals.
- Monitor project execution and promptly respond to changes and risks.
- Ensure coordinated teamwork among the entire team and stakeholders.
- Effectively utilize resources, including budget, time, and personnel.
IT projects, like any other projects, face risks and uncertainties that can have a negative impact on their successful completion. Below are some of the most common risks and uncertainties that IT projects encounter:
- Technical risks are related to technical complexities, insufficient team knowledge and experience, the selection of inappropriate technologies or tools, as well as potential technical failures and compatibility issues among different systems.
- Budget risks involve irrational budget allocation, unexpected expenses, overspending, inflation, and fluctuations in currency exchange rates, all of which can threaten the project's financial stability.
- Timeline risks arise from the need to meet tight deadlines, potential delays in project implementation, as well as dependencies on other projects and external factors that can significantly affect project success.
- Requirement changes. Uncertainty in client requirements or changes during development can lead to plan revisions and an increase in time and costs.
- Resource shortages. Limited availability of skilled staff, a lack of necessary equipment or software, can hinder project implementation.
- Errors and defects. Untimely detection and rectification of errors and defects can lead to significant system performance problems.
- Vendor dependence. Issues with vendors or external counterparts can impact project completion time and quality.
Business environment uncertainty. Changes in economic or political conditions, as well as various market factors, can affect project goals and expectations.
Risks and uncertainties in IT projects cannot be completely eliminated, but with proper planning, analysis, and management, their impact can be reduced, ensuring the successful completion of the project.
IT Project Team
The IT project team is a group of specialists united by a common goal: the successful implementation of the project. It comprises various roles and competencies such as developers, analysts, testers, designers, and other experts. The team must possess high levels of communication skills and open feedback. Each member should clearly understand their role in the project and contribute to its overall success.
Who is a Project Manager?
The project manager is the leader of the team, responsible for managing the IT department from concept to launch. Their role involves coordinating the team's activities, resource planning, risk management, and ensuring tasks are completed within set timelines and budget.
The core functions of project management include:
- Project Planning
Defining the project's goals, tasks, and activities necessary for achieving project success. This involves developing schedules and budgets, as well as identifying risks and action plans to minimize them. - Communication
Ensuring transparent and effective communication among all project participants, as well as liaising with clients and stakeholders. - Resource Management
Assigning tasks and responsibilities among team members, managing work hours, and ensuring access to necessary resources. - Progress Monitoring
Tracking task completion, overseeing timelines and budgets, and providing regular project status updates. - Risk and Conflict Management
Addressing emerging issues, managing risks, and resolving conflicts within the team. - Team Motivation
Supporting and motivating team members, fostering a positive work environment, and incentivizing goal achievement.
Stages of Project Management: From Idea to Launch
Managing IT companies involves several stages and constitutes a system of project management. These stages aid in transforming an idea into a successful project:
- Project Initiation
Defining objectives, justifying the project's necessity, and creating a brief project description. - Project Planning
Developing a detailed action plan, determining resources and timelines, as well as identifying risks. - Project Implementation
Executing the plan, coordinating team efforts, and managing resources. - Control and Monitoring
Tracking project progress, identifying and managing risks and changes. - Project Closure
Formally closing the project, evaluating its outcomes, and drawing lessons for future projects.
Methods and Tools for Project Management
There are numerous methods for managing IT projects, each of which is suitable for specific project types and teams. We will explore popular methods such as Scrum, Kanban, Waterfall, and Agile, and identify their characteristics and applicability.
Scrum
Scrum is a flexible methodology for managing IT projects, particularly popular in software development. Its main advantage lies in its flexibility and adaptability to changes, making it an ideal choice for projects with frequently changing requirements.
Key Elements of Scrum:
- Sprint
Each project is divided into short iterations known as sprints, typically lasting 1 to 4 weeks. The team selects tasks from the Product Backlog (project task list) and completes them during the sprint. - Scrum Master
A key member of the team responsible for ensuring adherence to the Scrum process, removing obstacles, and supporting the team. - Product Owner
Responsible for defining requirements and task priorities in the Product Backlog, as well as ensuring maximum product value. - Daily Scrum
Daily brief meetings where the team discusses progress, tasks, and obstacles.
Applying Scrum allows the team to quickly adapt to changes and achieve results throughout the entire IT project management process.
Kanban
Kanban is a methodology for managing IT enterprises, based on the visual representation of workflow and limiting the number of active tasks in various project stages.

Key elements of Kanban:
- Kanban Board
A visual representation of all project tasks, divided into columns representing stages of completion (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done). - WIP Limit (Work In Progress)
Setting a maximum number of active tasks in each column to avoid team overload.
Kanban enables the team to visualize the task execution process, manage workflow, and minimize response time to changes.
Waterfall
Waterfall is a traditional project management method in IT that involves a linear sequence of stages: initiation, planning, execution, testing, and deployment.
Key stages of Waterfall:
- Project Initiation
Defining project goals, requirements, and resources. - Planning
Developing a detailed action plan, including timelines and resource allocation. - Execution
Implementing tasks in accordance with the plan. - Testing
Verifying functionality and compliance of results with specified requirements. - Deployment
Final implementation of the product or project outcome.
The Waterfall approach is well-suited for projects with clearly defined requirements and low change costs. It provides a structured and sequential approach to project management, making it appealing for projects with limited uncertainties.
However, Waterfall has its drawbacks as well. One of the main disadvantages is the lack of flexibility to respond to changes in requirements or risks. If changes need to be made to stages that have already been completed, it can lead to delays and additional costs.
Agile
Agile is a broad family of flexible project management methodologies that emphasize rapid adaptation to changes, customer interaction, and delivering valuable outcomes.
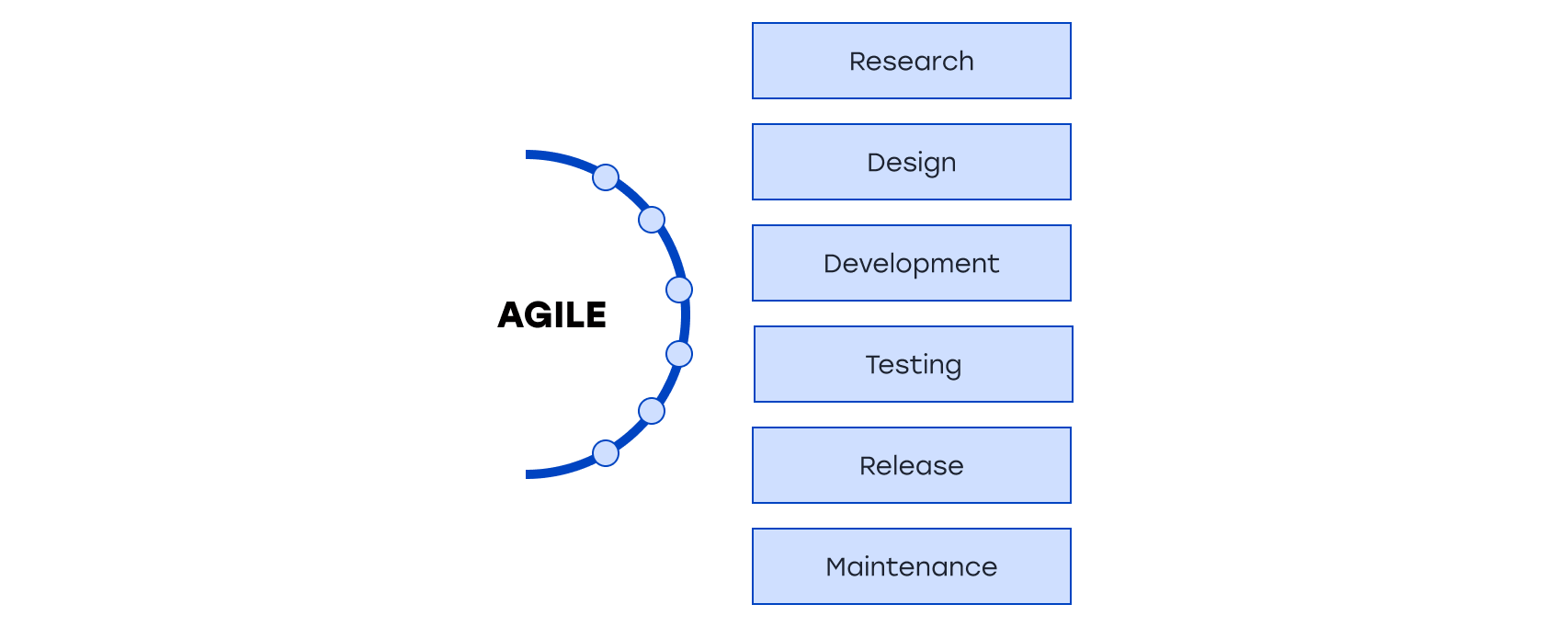
Key principles of Agile:
- Incremental Development
The project is developed and delivered gradually, in several small iterations. - Customer Collaboration
The customer actively participates in the development process, providing feedback and determining priorities. - Self-Organizing Teams
Teams have the freedom to choose working methods and make decisions. - Quick Results
Each iteration should lead to a functional and useful outcome.
Applying Agile allows teams to respond quickly to changes, deliver value to customers, and manage risks effectively.
How to Choose the Right Approach?
The choice of project management method depends on the specific characteristics of the project, its goals, and the team's attributes. If the project is characterized by frequent changes in requirements and high uncertainty, Scrum and Agile may be preferred choices.
If the project is well-defined with clear and unchanging requirements, Waterfall could be a more suitable option. If you need visualization of the work process and control over the workflow, Kanban can be a useful tool.
It's also important to consider the team's experience, skill set, and customer support when choosing a method.
How to Become a Project Manager
A project manager is the one at the helm, aiming to achieve project goals and persevering even in the face of challenges. Their role involves skillful project management and having a comprehensive view of what's happening. They serve as a support system for the entire team, enabling each member to focus on their tasks without being distracted by organizational matters. For instance, a designer need not worry about budgets, a tester can focus on text quality, and a developer can forget about project documentation. Additionally, a manager addresses problems, resolves conflicts, and locates resources where others may not.
To become such a superhero, you need to delve into project management theory and master all aspects of IT service management. You should also consider the following:
- Obtain education or work experience in the field of information technology. Solid knowledge in various IT aspects such as software development, systems administration, databases, and networking is a crucial prerequisite for working as an IT project manager.
- Practice managing small IT projects or tasks. This could involve developing a small software product, creating a website, or implementing a new information system. Gaining experience in IT projects will help you understand the processes and specificities of management in this field.
- Familiarize yourself with project management basics and various methodologies such as Scrum, Agile, Waterfall, and others. This will help you choose the most suitable approach for managing IT projects.
- Develop soft skills. A successful IT project manager needs good communication, leadership, and organizational skills. Focus on developing your ability to lead teams, resolve conflicts, and motivate employees.
- Deepen your IT knowledge. The IT field is constantly evolving with new technologies emerging. Stay updated on the latest trends and develop your expertise to be a competent and effective manager.
- Seek opportunities to manage real IT projects. This could be an internal project within your company or a freelance project. Real-world experience will reinforce your knowledge and develop practical skills.
- Consider finding a mentor or guide in the field of IT project management. Interacting with experienced professionals will provide valuable advice and guidance.
- Think about obtaining professional certification in project management, such as PMP or CAPM from PMI.
- Work on continuous improvement. IT project management is an ongoing process of learning and growth. Continuously enhance your skills and knowledge in this field.
- Remember that becoming an IT project manager requires effort and dedication. Be persistent and strive for development in this professional realm.
By following these steps and aspiring for constant growth, you can become a successful IT project manager and achieve career success in this engaging and sought-after field.